People generally use different forms of information in their day-to-day life. Their accessibility to information through digital media is also gaining much importance in various fields like office, library, and industries. In developing a system, it should be kept in mind that it is designed to satisfy the needs of the users. That is, the developed system should be human-centered and holistic. While forming the system for human use, more importance should be given to designing the software rather than giving importance to the hardware and other related systems.
The user-centered activities cover the entire development efforts and analyses the user’s requirements and their tasks and design the system accordingly. The system is also checked and evaluated based on the feedback of the users; therefore, the users play a very important role in the design of the input systems. In between the design and development is carried out, a validation test is also conducted to check the usability and also help in setting of precedence for training. The human factors or the users form an important in most of the system development activities like audience definition, task analysis, heuristic view, use case model, iterative design, and design specification and in the usability validation tests.
Discuss systems reengineering and how it is performed. Explain some of the tasks in system maintenance.
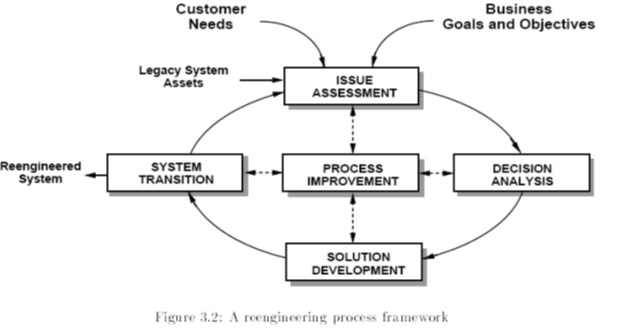
Systems reengineering could be defined to be the systematic transformation of an existing system into a new form to realize quality improvement in operation, system capability, functionality, performance, or evolvability at a lower cost, schedule, or rule to the customer.
There are three aspects that impinge upon systems reengineering.
- The current result
- The desired result
- Migration course
The very fact that the current results are available shows that engineering is already present, but there are certain lacunae that prevent it from being applied to its full potential or capacity. Thus the need for desired results or reengineering becomes necessary for the system to be fully operationalized through reengineering procedures and practices in order that the system is ridden of its inherent and acquired defects and fulfills the objectives for which it has been deployed.
The aspects of reengineering could be seen in the context of the following:
- Reengineering in successful organizations
- Reengineering without risks
- Reengineering as a strategic tool for business decision making
- Reengineering as a critical implement for best method use
- Envisioning
- process thinking
- systems thinking
- creative rethinking
- change management
- preparation
- reengineering for the future.
How it is used:
Reengineering is a hallmark for a successful and competitive organization that is able to make innovative changes for the improvement of its image and selling abilities, despite strong competitive forces operating in the current marketplace. It is enough needed to institute reengineering in terms of cost reductions, optimal usage of assets, personnel, and systems. Any lacuna could be redressed by reengineering and parity restored.
Next, it is seen that the risk element can be minimized through the use of reengineering in that outsourcing could be done instead of using own labor or systems, which could guarantee not only quality but also time factor in procedures. The next feature is that reengineering needs to be reassessed and updated to meet the current demands, in that as a strategic tool, using, for instance, ERP, Supply chain management (SCM), just in time methods (JIT), real-time inventory, etc. these are all strategic tools that management have at their disposal to tackle high costs of carrying inventory and investments in stocks, The next facet could be seen in terms of implementation of the best method that could address to lowest costs and highest profits, which is the need of business, by ethical means.
The best practices could be seen in terms of not cheating or defrauding customers or suppliers, exercising restraint in fact of provocation, being loyal to staff and employees, and genuinely caring for them; envisioning is important because goals and objectives are best achievable when seen in black and white; the company needs to have clear plans and forecasts on what it plans to do in the future, near and far, in order to align itself to achieve them. The next characteristic has to do with process thinking. It is seen in most concerns that the management may not be happy about the process. They feel that it is too lengthy or slow and therefore introduces systems by modifications of certain methods or procedures. This involves an element of reengineering since existing systems are replaced with newer and more efficient ones that could address the problem better and provide workable solutions.
It is necessary that enlightened managers need to think of systems or processes in order to achieve reengineered benefits. The present systems or processes are often blamed, so it becomes necessary to change them for better noel and innovative ones. This aspect is also taken up by reengineering, whereby systems are remodeled or renovated to suit modern conditions of operations.
Fine-tuning with progression and innovation
Therefore it could be said that reengineering sets in a new set of processes for work processing. Under reengineering, it is possible to overhaul the staffing arrangements whereby retraining obviates the need for seeking fresh recruits in place of existing ones. This is because the skill sets are already present but need to be upgraded and modernized to meet current requirements. Outdated theories and practices are abandoned, and reengineering ushers in new, dynamic, and innovative systems that are in tune with current times and reverse engineering requirements. It is very much like a rejuvenation of organizational structure and work practices to meet current demands and needs.
In the context of software, reengineering would renovate the current architecture and software models either through innovative methods or fresh solutions that could be envisaged and implemented. The objective of reengineering, therefore, could be seen in terms of availing of current business opportunities by fine-tuning and upgrading technological frameworks.
Case oriented basis
Systems reengineering is basically concerned about the fact that certain systems may not be able to meet practical or performance needs and, therefore, need to be modified or replaced with more relevant and promising techniques and systems. In some cases, it is needed only to make modifications keeping the basic inputs intact, whereas, in others, it may be necessary to change the raw data itself, depending upon situational demands and environmental needs.
All these are based on a case-to-case basis, on the merits of the actual situation, and no hard and fast rules can be evolved in the induction and deployment of systems reengineering. It is for the Board of Directors of the company along with specialists consultants who need to consider and implement the various aspects of systems reengineering, based on their knowledge and expertise of present and perceived corporate circumstances and, in their opinion, which set of systems would work best under given situations.
The architectural transition has to be smooth
However, there are certain aspects of systems reengineering that need to be kept in mind. The existing business data needs to be retained as much as possible in order to answer critical queries at later stages. The migration from the present to better and more sophisticated technology is hallmarked and desired objective of systems reengineering. This is important since the transition from one technological system to another has to be smooth with minimal compromise of data, and it is also important that as a result of reengineering and integration into new technological systems, the total originality and retrievals mechanism is not totally lost.
For example, if a premier banking company decides to migrate to a more sophisticated, accurate, foolproof, and faster technology, it is necessary that the revamping does not entail compromising with existing data, since this may be required for audit or archiving purposes or even form the basis of statistical data for the Central bank. The migration needs to be for better and more efficient overall performance, which needs to be ensured on a long-term basis. For best results, the benefits of systems reengineering need to be felt throughout the organization and not necessarily in a particular segment alone. This could also be seen in the fact that unless it is empirically tested and certified, the new systems may not be credible and thus needs to be shelved, at least for the present.
This stems from the fundamental axiom that SE should ensure more benefits than threats. As a matter of fact, the threats need to be minimal and controllable in order to reduce losses and enhance gains and benefits. Migration from one software application system to another could set the trend for higher performance, profitability, and progress, there is no doubt about it; but the negative aspects also need to be worked out, in terms of the fact if the system cannot be operationalized and implemented as expected. Thus, it is necessary to deliberately consider all aspects before a final solution is worked out since anything could be possible and nothing impossible in the corporate world. “Lower costs and more advanced functionality, contributing to an increase in the satisfaction of users, ease of management and business economics.”
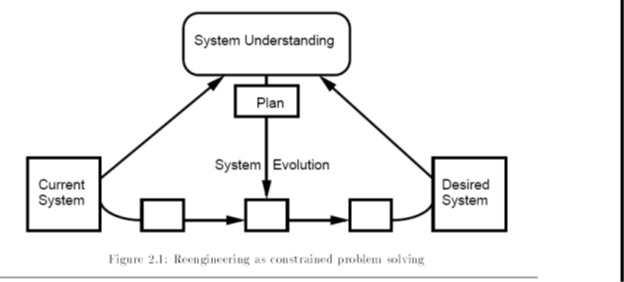
How to improve MIS
“For the information system to serve effectively and efficiently as time goes by, there are two ways to improve it. Firstly, re-design the whole system by using new technology and new database models; secondly, introduce a method that will make use of the existing systems to the maximum extent while the new requirements are still satisfied, i.e., Information systems reengineering.”