Background
The COVID-19 pandemic became an event which disrupted the normal way of life and forced all countries on the planet to adjust to new circumstances (Stefana, 2020). Businesses also were hit by the effects of the pandemic, which included not only hundreds of thousands of people being unable to work but also government restrictions (Nicola, 2020). The pandemic hindered the operations of global supply chains, decreased overall trade among nations, and put numerous firms in a situation where they had to experience financial losses (Guan, 2020). As a result, businesses had to find new innovative ways to continue functioning as usual to avoid bankruptcy and deliver value to their customers (Didier, 2021). Technological solutions such as virtual reality and telecommuting ultimately allowed people to work remotely and perform some of their tasks in order to ensure that their company is continuing to operate. The surge in demand for the two phenomena made many companies reconsider their inner operations and continue using a new approach to work even after the COVID pandemic (Manokha, 2020). Thus, it becomes interesting to evaluate the potential entrepreneurial opportunities concerning virtual reality and remote working in the period after the end of the pandemic.
The theoretical context of the current project involves utilizing the most relevant research frameworks necessary for ensuring thorough exploration of all concerning the main subject. The research will rely on entrepreneurship theories such as opportunity-based entrepreneurship theory and need for achievement theory. Additionally, the project will utilize qualitative research and will imply conducting an assessment of the existing opportunities from the perspective of transformational entrepreneurship.
In terms of the practical context, the research will focus on the organization and sectors which became the primary beneficiaries of virtual reality and remote work during the pandemic. Essentially, the project will explore the entrepreneurial opportunities of companies and industries which used the event of the pandemic as a catalyst for exploring new ways of operating. Subsequently, the concrete businesses and sectors which will be subjects of the study will be identified during the actual research.
As mentioned earlier, the COVID-19 pandemic became a major factor which disrupted the operations of thousands of companies on the planet (Nicola, 2020). As a result, many businesses turned to virtual reality and remote work as means to ensure stability (Vargo, 2021). The currency of the research concerns the necessity to determine the entrepreneurial opportunities which will be available to companies and individuals after the COVID-19 pandemic. It is clear that numerous businesses had considerable financial losses due to the circumstances associated with the pandemic. Yet, some companies managed to embrace a new approach with the help of virtual reality and remote work, elements which helped them achieve a competitive advantage (Vargo, 2021). The current research will analyze the available data on the existing cases of implementation of virtual reality and remote work and, based on evidence, will identify potential entrepreneurial opportunities for other businesses.
As a result, the value of the current research will be most apparent for companies which did not implement virtual reality and remote working and would like to know about entrepreneurial opportunities associated with them. The possible outcomes of the project will involve determining the business circumstances conducive to a successful implementation of virtual reality and remote work. Additionally, the research will focus on identifying possible ways to improve the existing solutions and creating a database of companies which introduced virtual reality and remote work.
Research Questions, Aims & Objectives
The project has a strong hierarchy consisting of the main research question, aims, and objectives which have to be accomplished in order to attain successful results.
Research Question
Thus, the primary research question of the project is following:
“Which entrepreneurial opportunities in the realm of virtual reality and remote work can businesses utilize in the post-COVID-19-pandemic period?”
Guiding Questions
Additionally, the research will rely on guiding questions which will reflect the key subject of the research and will let determine the scope of the study more accurately. These are:
- “Which virtual reality and remote work solutions did businesses during the COVID-19-pandemic period use?”
- “What will be the demand for virtual reality and remote work solutions among businesses during the post-COVID-19-pandemic period?”
Research Aims
- Identifying entrepreneurial opportunities concerning virtual reality and remote working in the post-COVID-19 era.
- Creating a list of industries which will benefit from embracing virtual reality and remote working solutions in the post-COVID-19 period.
Research Objectives
- Establishing the list of companies which started using virtual reality and remote working solutions during the COVID-19 period.
- Assessing the potential future use of virtual reality and remote working based on the current state of these fields.
- Exploring the demand for virtual reality and remote work solutions in the post-COVID-19 period.
- Evaluating the efficiency of the existing approaches to virtual reality and remote work and assessing their applicability in the post-COVID-19-period.
Literature Review
The literature review is an essential part of the current project since it ultimately allows the researcher to discover sources containing relevant information. All sources chosen for the review were found in various databases, including Google Scholar, JSTOR, and Scopus. Such choice of resources was justified by the fact that they contain scientific, peer-reviewed studies and articles. The primary search procedure involved utilizing keywords such as virtual reality, remote work, pandemic and technology, to find relevant sources. All of the sources used in the review were chosen because they contributed to the creation of an array of information and data necessary for the successful completion of the project.
As mentioned earlier, in this project, the concept of entrepreneurship does not concern creating or developing a new company from the start. The paper relies on the idea of entrepreneurship as a necessary element for innovation and growth; some researchers call it corporate entrepreneurship ( (Perez, 2016) (Umrani, 2018); (Burns, 2013)). Such an approach ultimately lets companies demonstrate excellent performance by being able to always adjust to new challenges and circumstances. To attain excellence, entrepreneurship must rely on knowledge management which implies three tasks: leveraging, extending, and importing knowledge (Kazanjian, 2017). Following these three objectives helps businesses process information and based on it, make decisions on implementing innovative approaches.
When discussing entrepreneurship, it is essential to explore theories which exist in this realm to gain a better understanding of the subject. The opportunity-based entrepreneurship postulates that entrepreneurs do not have a capacity to cause changes but can effectively exploit them as opportunities (Simpeh, 2011) (He, 2020). In other words, businesses rarely can influence the world and instead must respond to various external triggers and events. As noted by Dimitratos et al. opportunity-based entrepreneurship espouses orientation towards international learning and discovering novel approaches which can ensure attainment of competitive advantage (Dimitratos, 2016). Subsequently, it becomes important for companies with entrepreneurial attitude to seek new solutions to the problems they face.
The need for achievement theory is another framework which is worth exploring in detail since it offers valuable insights into entrepreneurship. The theory claims that entrepreneurs are always striving to achieve new heights and excel in their field of work ( (Sujarwo-et-al, 2020); (Acquah, 2021)). As a result, entrepreneurs are motivated to implement innovative solutions to improve the operations of their businesses and ensure better communication in the team. As studies demonstrate, the need for achievement has a positive correlation with entrepreneurial behaviour (Haroon, 2020). Thus, when assessing the activity of certain companies, researchers should attempt to establish to which extent the company’s changes were motivated by the owners’ need for achievement.
Seeing opportunities always entails making strategic decisions with an intention to improve the company’s performance. The strategic orientation approach constitutes a set of various principles which can govern businesses in their process of increasing value for clients and detecting opportunities ( (Kocak, 2017); (Kakapour, 2016)). Essentially, strategic orientation is a framework which allows businesses to align their objectives with the existing opportunities. Yet, such an approach is also applicable to scientific research to recognize entrepreneurial opportunities and assess their viability (Tuomisalo, 2019). The strategic orientation approach is valuable for the current project because it will contribute to the methodology and will be used as part of it.
The COVID-19 pandemic can be considered a crisis which negatively impacted entrepreneurs worldwide and made them embrace new opportunities to continue working. Yet, a period of crisis also constitutes the perfect time for embracing innovation and novel approaches because, during them, customers shift their needs (Am, 2020). In this sense, the coronavirus pandemic is similar to previous crises, including the financial one which occurred in 2008 and lasted several years (Oravský, 2020). Studies demonstrate that companies which can maintain an appropriate level of innovation, as well as proper internal and external knowledge capabilities, are able to reduce the effect of financial crises on their enterprises (Zouaghia, 2018). Such evidence shows the necessity for businesses to adjust to new circumstances using the latest technologies. The COVID-19 enabled numerous companies to embrace virtual reality and remote work as means to continue operating (Vargo, 2021). Information and communication technologies which form the basis of the two aforementioned phenomena were discovered to increase organizational performance (Yunis, 2018). Thus, there is a possibility that these technological solutions can continue delivering positive results for companies even after the end of the pandemic and will provide them with new entrepreneurial opportunities.
Another important theory which needs to be explored is transformational entrepreneurship and its role in the world during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. The concept of transformational entrepreneurship concerns the participation of businesses in society and their need to address challenges such as economic underperformance, unemployment, and societal evolution (Jones, 2019). Studies demonstrate that transformational entrepreneurship can positively impact the readiness of organizations to embrace change and maintain a high level of performance (Chrisanty, 2021). Yet, transformational entrepreneurship always depends on the activity of managers and owners of companies. Therefore, there is also a necessity to present the idea of transformational leadership, which ultimately concerns the ability of organizational leaders to motivate employees and discern future trends (Ratten, 2018). The COVID-19 pandemic forced many people to encounter challenges, and the role of businesses was to alleviate them with the help of remote work and virtual reality.
Research Design & Methodology
Methodology
The current research project will espouse several key methods necessary for exploring the main subject and meeting all the research objectives. The Saunders Research Onion Diagram was chosen as model for designing the research methodology. It provides a detailed assessment of all project stages and it fits the current case-study research. The project will involve conducting qualitative research, which will be based on the collection of data on the implementation of virtual reality and remote work during the pandemic. The data will include scientific journals, business reports, online publications, recent statistics on the performance of different sectors of the economy, as well as organizations’ websites. The project will utilize stratified sampling since it involves dividing a population into several mutually-exhaustive groups based on their features (Arnab, 2017). There are many companies which will be included in the study and the aforementioned sampling design will help divide them into groups based on their industries and will ensure equal representation. Based on the fact that all data chosen for the current research will be secondary, the search will be conducted using the Internet. The data analysis type will be descriptive and will focus on accurately listing and assessing all of the aspects of the topic and; therefore, the approach will be inductive (Saunders, 2019). Overall, the study will be interpretivist since it reflects the main aim of explaining the entrepreneurial opportunities of businesses in the realm of virtual reality and remote work. Case-study will be the primary strategy of the research since it will deal only with secondary sources and will involve describing them. The study will espouse mono-method since it will be based only on one method, and it will be cross-sectional, drawing information from multiple sources.
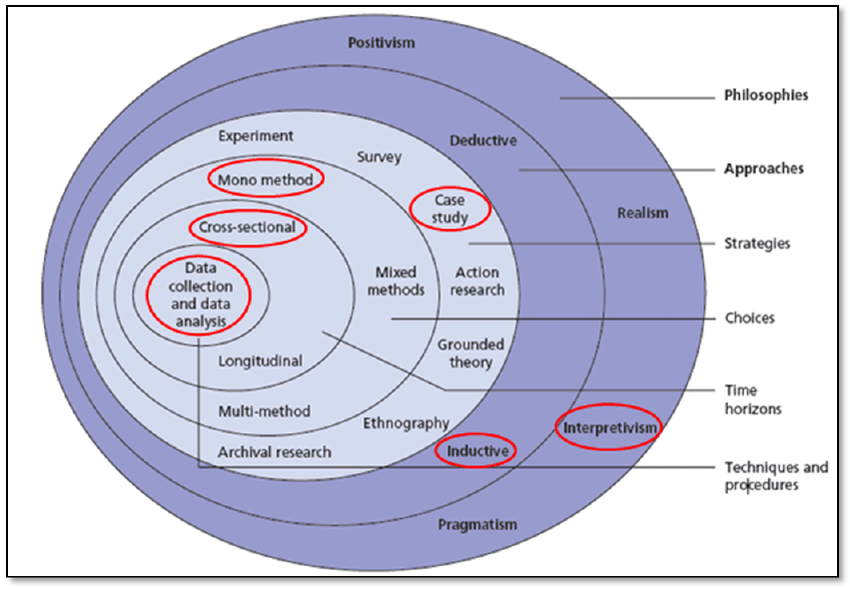
The research will be based on the use of the strategic orientation approach to identify entrepreneurial opportunities in the spheres of virtual reality and remote work. The project will rely on the research conducted by (Tuomisalo, 2019), (Kakapour, 2016), (Kocak, 2017), who previously implemented the aforementioned approach in their studies. As a result, strategic orientation must help determine the level of success of introducing virtual reality and remote work and to consider entrepreneurial opportunities linked to them.
Constraints
One potential constraint to access to data can be the absence of authorization to view private data of the organizations explored in the research.
Ethical Issues
There are currently no apparent ethical issues associated with the project, except for potential legal ramifications in case of unauthorized access of companies’ data which is unlikely.
Project Plan
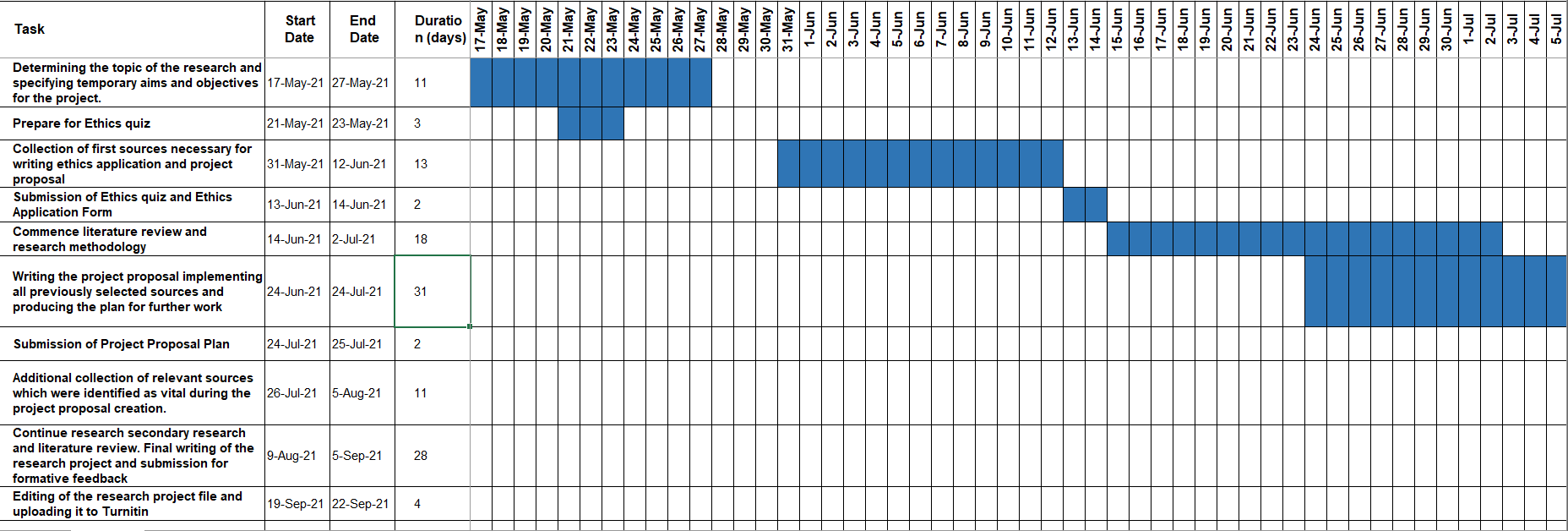
The first stage will involve determining the basic topic, establishing the first aims and objectives for the project, preparing and taking the ethics quiz, which will take about fourteen days. During the following step, the focus will be given to the process of collecting initial sources, the submission of the ethics quiz and ethics application form this will last fifteen days. Literature reviews and research methodology commences in the next stage which will be used in developing the research proposal and determining the action plan; this will take forty days as it will require a thorough analysis of sources.
The project plan will act as the foundation for the research, and it will ultimately demonstrate the existing gaps and requirements. Thus, the following stage will involve the collection of additional sources and data for the research, which will take eleven days. Finally, writing if the research project will take twenty-five days and four days will be allocated to editing to ensure excellent quality. Overall, the research will take a hundred and eleven days; it will be ready by September which is the deadline for this project.
Risk Management
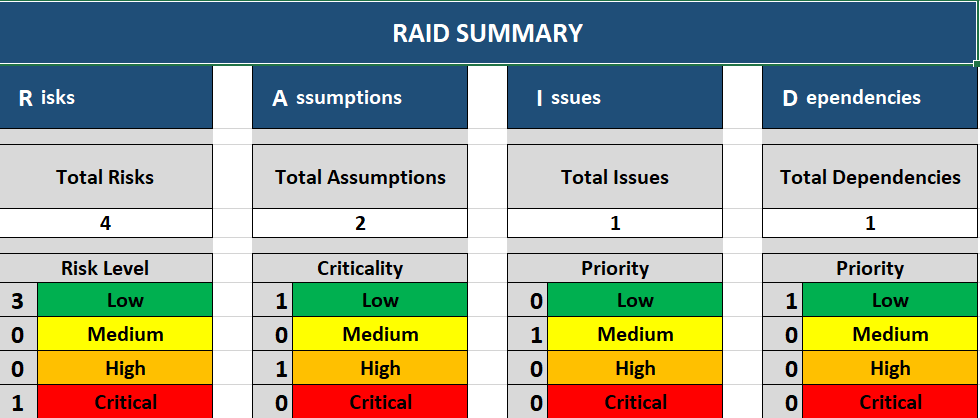
The current project does not imply encountering any serious risks now, yet there is always a chance of such, and the risk management tool – RAID can help to prevent it.
Risks –The primary potential risk for the current project concerns the absence of a sufficient number of appropriate sources and data necessary for conducting the research. Additionally, a potential risk may relate to the low quality of resources chosen for the research. Moreover, there is also a possibility of failure to produce an effective methodology to analyze the existing data and make conclusions based on it. All three risks have a low probability of occurrence, yet they will negatively impact the project to a considerable extent if they emerge. Nevertheless, during the research, the risk of possibility of not finding relevant sources should be given the utmost priority.
Assumptions – The main assumption concerning the project is that the research will be successful because there are numerous theoretical sources which can be used to develop the methodology of the project. Another assumption rests on the fact that the area of virtual reality and remote work have been particularly prominent during the pandemic and, therefore, there will be enough data on companies’ activity in these spheres. Both assumptions can be easily validated through a search of data and sources, yet the first one should be given priority.
Issues – There are currently no issues associated with the project since during all of the stages which have already been executed, the research did not encounter any problems. Thus, there are only potential issues which can emerge because of poor risk management.
Dependencies – The only dependency of the current project is the access to certain documents and data which can be restricted. Yet, there are measures which can be taken to prevent such a situation.
References
Acquah, A. e. (2021). Literature review on theories of motivation. EPRA International Journal of Economic and Business Review, 9(5), 25–29.
Am, J. B. (2020). Innovation in a crisis: why it is more critical than ever. Web.
Arnab, R. (2017). Survey sampling theory and applications. Academic Press.
Burns, P. (2013). Corporate entrepreneurship: innovation and strategy in large organisations.. 3rd ed. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Chrisanty, C. e. (2021). The role of transformational entrepreneurship, readiness to change and counterproductive work behavior in enhancing employee performance. Organizacija, 54(1), 63–81.
Didier, T. H. (2021). Financing firms in hibernation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Financial Stability, 53, 1–14.
Dimitratos, P. e. (2016). SME internationalization: How does the opportunity-based international entrepreneurial culture matter?’. International Business Review, 25(6), 1211–1222.
EPM. (n.d.). Expert Program Management. Web.
Guan, D. (2020). Global supply-chain effects of COVID-19 control measures. Nature, 4, 577–587.
Haroon, A. a. (2020). Need for achievement as a predictor of entrepreneurial behavior: The mediating role of entrepreneurial passion for founding and entrepreneurial interest. International Review of Management and Marketing, 10(1), 40-53.
He, J. e. (2020). Opportunity-based entrepreneurship and environmental quality of sustainable development: a resource and institutional perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production, 256, 1–12.
Jones, P. a. (2019). Conclusions on transformational entrepreneurship. in Jones, P. and Maas, G. (eds.) Transformational entrepreneurship practices. New York: Springer, 105–113.
Kakapour, S. e. (2016). Antecedents of corporate entrepreneurship in Iran: the role of strategic orientation and opportunity recognition. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, 28(3), 251–266.
Kazanjian, R. K. (2017). Implementing strategies for corporate entrepreneurship: A knowledge-based perspective. In Hitt, M. A. et al. (eds.) Strategic entrepreneurship: Creating a new mindset. Hoboken: Wiley, 173–199.
Kocak, A. C. (2017). Market, entrepreneurial, and technology orientations: impact on innovation and firm performance. Management Decision, 55(2), 248–270.
Manokha, I. (2020). Covid-19: Teleworking, surveillance and 24/7 work. Some reflexions on the expected growth of remote work after the pandemic. Political Anthropological Research on International Social Sciences (PARISS), 1, 273-287.
Nicola, M. e. (2020). The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review. International Journal of Surgery, 78(1),, 185–193.
Oravský, R., Tóth, P., Bánociová, A. et al. (2020). The ability of selected European countries to face the impending economic crisis caused by COVID-19 in the context of the global economic crisis of 2008. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2020, 13(8), 179-196.
Perez, M. A. (2016). Entrepreneurial opportunities perception and intentions within European innovation-driven economies under the shadow of a financial crisis’, in Bilgin, M. H., and Danis, H. (eds.). Entrepreneurship, business and economics vol. 1. New York: Springer,, 3–15.
Ratten, V. a. (2018). Transformational entrepreneurship. London: Routledge.
Saunders, M. L. (2019). Research methods for business students.. 8th. edn. London: Pearson.
Simpeh, K. N. (2011). Entrepreneurship theories and Empirical research: A summary review of the literature. European Journal of Business and Management, 3(6), 1–8.
Stefana, A. Y. (2020). The COVID-19 pandemic brings a second wave of social isolation and disrupted services. European archives of psychiatry and clinical neuroscience, 270(6), 785–786.
Sujarwo-et-al. (2020). Do affective commitment, competency and Deming cycle affect. European Journal of Business and Management, 10(8), 1–6.
Tuomisalo, T. (2019). Emergence of an entrepreneurial opportunity: a case within a Finnish telecommunication international new venture. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 17, 334–354.
Umrani, W. A. (2018). Corporate entrepreneurship and business performance: the moderating role of organizational culture in selected banks in Pakistan. PSU Research Review, 2(1), 59–80.
Vargo, D., Zhu, L., Benwell, B., & Yan, Z. (2021). Digital technology use during COVID-19 pandemic: A rapid review. Human Behavior with Emerging Technologies, 3(1) , 13–24.
Yunis, M. T. (2018). The role of ICT and innovation in enhancing organizational performance: The catalysing effect of corporate entrepreneurship. Journal of Business Research, 88, 344–356.
Zouaghia, F. S. (2018). Did the global financial crisis impact firms’ innovation performance? The role of internal and external knowledge capabilities in high and low tech industries. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 132, 92–104.
