Introduction
The aim of every organization is to maximize profit while minimizing costs. The operations of an organization in a given business environment aims at ensuring that the organization achieves its objectives. Financial performance of an organization is important for investors. However, it is not the only measure of the performance of an organization. This study examines the performance of the three banks, U.S. Banks, Wells Fargo Bank, U.S. Bank and JP Morgan Chase Bank, with the aim of advising investors on the best investment bank. The study will focus on the comparison of the financial statements of three banks in terms of their income, assets and projected future performance based on the analysis of the statements. The focus on the financial performance of the banks would end up with recommendations on the best option for investors to invest in. (Uniform Bank Performance Report).
Bank Profiles
Wells Fargo Bank
The Wells Fargo Corporation dates back in 1852 when Henry Wells and William Fargo established the corporation that offered banking services to customers that rushed for gold, which was used as a medium of exchange. Since its establishment, the company has been able to maintain its original brand name in the course of all its business operations. With the experience in satisfying its customers’ financial needs, the company has been able to thrive for many years providing and helping its clients succeed, given its mission statement of “Together we go far”.
The U.S. Bank
The U.S Bank is a subsidiary of the U.S Bancorp that is headquartered in Minneapolis in Minnesota. The bank is rated as the sixth largest bank in the U.S and provides financial services while acting as a holding company. Unlike many other banks, the bank does not have a long rich history since the current bank was established through the combination of regional banks that were in operation in Midwest and West in the 1990s. The banks that formed the bank had growth though various means such as mergers and acquisitions. The services offered include consumer banking, wholesale banking and premium financial products and services.
JP Morgan Chase Bank
This is a U.S based multinational corporation that provides financial services in many countries throughout the world. The bank is headquartered in New York and has many subsidiaries in other states and countries. Other services offered by the firm include private equity, services in treasury and securities, retails financial services and card services among many other products and services. JP Morgan has a rich history that is characterised by experience in various businesses with growth and expansion being achieved in various ways such as mergers and acquisitions. In addition, the bank boasts having the experience of operating in diverse business environments and cross-cultural boarders given that it can trace its roots in both the U.S and the UK.
Financial Analysis
This section examines the financial performance of the three bank in terms of their revenues, incomes statements and assets. Financial ratios will be utilised in the financial analysis in order to determine the performance and comparison of the banks.
Important Ratios
Comparison of the two companies’ ROA in the above figure indicates that the ROA of Goodman Fielder fluctuated over the five-year period first taking a downfall before beginning to rise. However, the ratio of Elder Ltd only fell slightly before registering a steady increase. This indicates Goodman Fielder as having a higher ROA compared to Elder Ltd.
ROE
Funding activities of the organization usually involves the owner’s equity and shareholder’s equity. This ratio indicates the level of income generated on the shareholder’s funding. Thus, it reveals the profit realized by an organization from the investment made by the company’s shareholders.
Efficiency Ratios Comparison
Inventory Turnover
This ratio indicates the period taken to convert the company’s inventory into revenue. The figure below indicates the comparison of the inventory turnover for the two companies (Moyer, McGuigan, & Kretlow, 2001).
Asset Turnover
Assets turnover as a ratio provides a relationship that exists between the assets of an organization and the revenue realized by the organization. The ratio indicates the sales generated from each dollar of assets. The comparison of the ratio of the two companies is illustrated in the figure below.
Liquidity ratios
Current ratio measures the ability of the two firms to meet their short-term obligations as they fall due. Three ratios were used to measure the ability of Elder Ltd and Goodman Fielder Ltd to meet their short-term obligations as discussed below.
Current Ratio
The current ratio indicates the speed at which an organization can meet its obligations in the short term. A higher current ratio is usually preferred to a lower ratio because a higher ratio indicates a higher capability of the firm to meet its short-term obligations using its current assets.
Debt to Equity Ratio
The debt to equity ratio makes a comparison between the owner’s equity and the funds that are borrowed from shareholders. Thus, many firms to measure the financial advantage hence providing the extent to which the organization needs to fund its activities using the owner’s equity against the capital provided by investors utilize it (Ross, Westerfield & Jordan, 1998). A high gearing ratio is usually not encouraged since it indicates risky investments or operations for the firm and investors.
Company Ratio Comparisons
Every organization aims at maximizing its profitability hence minimizing all costs. The comparison of the profitability of Wells Fargo Bank, U.S. Bank and JP Morgan Chase Banks was through examination of the Return on assets and return on equity of the two companies. This section compares the ratios of the banks in terms of their profitability, assets and efficiency.
Wells Fargo Bank
Table 1
The above table 1 indicates the comparison of the financial ratios of Wells Fargo bank for the 2010 and 2010 financial periods. ROA measures the income that an organization realizes on its assets. As an efficiency ratio, ROA indicates effectiveness of the management of Wells Fargo Bank in managing the bank’s assets to generate revenue. The ratio provides the earnings generated from the capital that was invested by the firm. From the above table, it is evident that the ROA ratio of the bank for the two financial periods is almost constant although it increased by a margin of 0.06 to reach a high of 1.2 in the 2011 financial period. The ratio indicates an increase in returns on the assets of the bank for the two financial periods (U.S Bank, 2011).
The other ratio is the ROE that is of great concern to investors since Funding activities of the organization usually involves the owner’s equity and shareholder’s equity. This ratio indicates the level of income generated on the shareholder’s funding. Thus, it reveals the profit realized by an organization from the investment made by the company’s shareholders. From the table, the ROE for the Wells Fargo bank remained a constant after a reduction of 0.02 in 2011 from 11.92 in the 2010 financial period. The ratio in the table above indicates that investors’ equity earns the company high returns.
Assets turnover as a ratio provides a relationship that exists between the assets of an organization and the revenue realized by the organization. The ratio indicates the sales generated from each dollar of assets. The comparison of the ratio of the two companies is illustrated in the figure below. The data in the above table provides the assets turnover for Wells Fargo and it indicates that the asset turnover for the bank remained fairly constant for the two at 0.07 in 2010 and 0.06 in 2011 (Wells Fargo, 2011).
The debt to equity ratio makes a comparison between the owner’s equity and the funds that are borrowed from shareholders. Thus, there are many firms to measure the financial advantage hence providing the extent to which the organization needs to fund its activities using the owner’s equity against the capital provided by investors utilize it (Ross, Westerfield & Jordan, 1998). A high debt to equity ratio is usually not encouraged since it indicates risky investments or operations for the firm and investors.
The net interest income of an organization is of great importance to an organization as it determines the differences between the revenues generated by interest bearing assets of the bank and the cost incurred in servicing the bank’s liabilities. Given the data on Wells Fargo in the table above, it is evident that the net interest income of the bank improved from -18.49 to -10.81, an indication of improved performance.
The U.S Bancorp
Table 2
The above table 2 provides ratios that indicate different performances of the U.S Bank for the 2010 and 2011 financial periods. From the table, the bank did well in its income earned from its assets as the ratio indicated an increase from 1.3 in 2010 to 1.4 in 2011. The increase in return on assets could also be used to explain the increase in the return on the capital invested by investors. The ROE of the bank increased from 12.8 in 2010 to 15.2, a sign of good performance. Given that most investors are attracted by the returns they obtain on their investment, then the increase in ROE could attract many investors to invest in this bank. In addition to the ROE and ROA, assets turnover could also be used by some investors in determining the profitability of the organization in terms of its assets. The assets turnover for the bank is remained constant over the two periods indicating that income realised from the assets of the bank did not improve (JP Morgan, 2011).
The debt to equity ratio is a useful ratio as it helps in determining the debts of the bank in relation the equity of the bank. Investors turn to this ratio to establish their level of investment in the firm. A high level is discouraged. Therefore, the above table 2 data indicates that this ratio increased from 1.14 in 2010 to 1.89 in 2011, an indication of increased debt. Net interest income of U.S bank increased from -24.28 in 2010 to -14.91 in 2011.
JP Morgan Chase Bank
Table 3
The ROE of the company improved from 9.69 in the 2010 financial period to 10.9 in 2011 period. The increase in the ROE of the company is a good sign for investors since they could reap higher income for their invested capital. The company also reported increased returns on assets that increased from 0.76 in the 2010 financial period to 0.09 in the 2010 period. The assets turnover indicates constant returns of 0.5 for the two periods. However, the firm registered increased debts compared to the equity of the bank as indicated by an increase in debt to equity ratio. The ratio increased from 1.81 in the 2010 financial year to 4.05 in the subsequent period of 2011. Continued increase in the debts of the firm in relation to the equity of shareholders could discourage investments from investors. Moreover, the net interest income of the bank improved from -16.2 in 2010 to -8.28. (Rivlin, 2010).
Comparison of the three banks using their Net Income and Assets
Net Income Comparison
Table 4
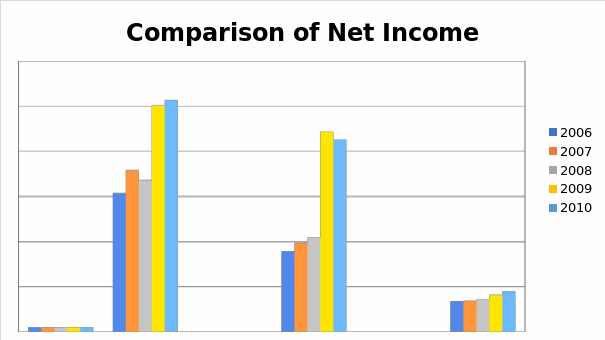
The above data compared the three banks using their net income. From the above data in table 4 that was used to generate fig 1, it is evident that the net income for all banks increased over a five year period from 2006 to 2010. JP Morgan Chase Bank indicated fluctuations in the net income between 2006 and 2008 where its revenue increased from $61,437 million in 2006 to $71,732 million and $67252 in 2007 and 2008 respectively. The bank turned around its performance to end up improving and increasing its net income to $100,434 and $102,694 in 2009 and 2010 respectively. (Connor et al., n.d.)
On its part, Wells Fargo Bank indicated a continuous increase in its revenue that kept on increasing from $ 35691 in 2006 to $88686 in 2009 before declining to $ 85210 in the financial period that ended in 2010. This is a good financial performance that every investor would admire. The U.S bank also indicated a continuous growth in its net income for the five year period with the net income increasing from $13,587 million in 2006 to $17,939 million in 2010. When it comes to the comparison of the values of net income, JP Morgan Chase bank has the highest figures for its net income followed by the Wells Fargo Bank and lastly, the U.S Bank.
Assets Comparison
Table 5
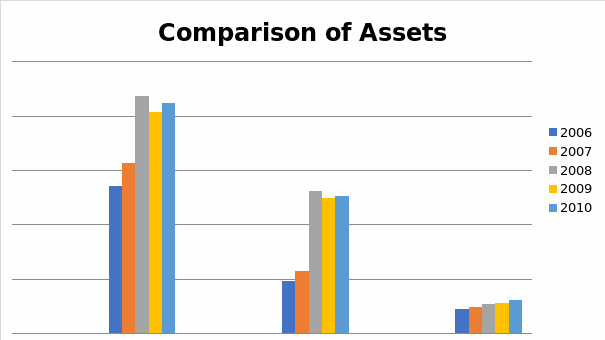
The above table and figure compares the assets of the three banks over a period of five years. The JP Morgan Chase Bank indicated progressive increase in its assets for the first three years before fluctuating in the subsequent two years. The assets of the bank increased from $1,351,520 to $2,175,052 in 2008. However, the assets decreased to $2,031,989 in 2009 before increasing again to $2,117,605 in the 2010 financial period. Wells Fargo also indicated similar results with increase in the total assets in the first three periods (2006, 2007 and 2008) with fluctuations in the last two years. The Bank’s assets increased from $484,996 in 2006 to $1,309,639 million in 2008 before decreasing to $1243626 million in 2008. However, the assets increased to $ 1258128 million in the 2010 financial period. In comparison to the two companies, the U.S Bank increased progressively for three periods with the assets increasing from $219,232 in 2006 to $307,786.
When comparing the values of the assets, the JP Morgan Chase bank still has the highest values of assets compared to the other two banks. The U.S Bank has the lowest values of assets. (Investment Banking)
Overall Comparison
The above comparison of assets and net income of the banks reveals that JP Morgan Chase Bank is the best investment destination for all investors given its high values for net income and assets. Investors concerned with progressive growth could end up investing in the U.S bank that has shown progressive increase in its net income and assets over the five year period. If the assets and income comparisons are to go by, JP Morgan Chase Bank and Wells Fargo Banks will continue to depict fluctuating increases in their values of assets and net income while the U.S bank would keep on increasing its growth in assets and net income therefore making the bank the best investment destination. (Nationals People’s Action, 2010).
In spite of the comparison of net income and assets, investors should compare the performance of the companies using their financial ratios. The comparison of the banks using ROE indicates that JP Morgan Chase Bank has the lowest ratio that is at 10.9 for the 2011 financial period while the U.S Bank has the highest values of the ratio for the similar period. This is an indicator that investors could prefer investing in the U.S bank compared to Wells Fargo bank and JP Morgan Chase bank due to the high values of ROE ratio. The ROA ratio comparison reveals that JP Morgan Chase Bank has the lowest values with the U.S bank having the highest values, thereby signifying reason for investment in the bank. The trend is similar for assets turnover in which the U.S bank and wells Fargo bank have the highest values of 0.6 compared to 0.5 values of the same ratio for the 2010 financial period for JP Morgan Chase Bank.
Concerning the debt to equity ratio, JP Morgan Chase bank has the highest value of 4.05 for the 2010 financial period while the Wells Fargo bank has the lowest figure of 1.34. In conclusion, the U.S Bank proves to the best investment destination for investors who would like to reap from their investments
References
Connor K., & Skomarovsky M. (n.d.). How the Biggest Banks are Bankrolling the Payday Loan Industry. Web.
Investment Banking (n.d.). 2011, Web.
JP Morgan, (2011). JP Morgan Chase Bank: Annual financial performance. Web.
Moyer, C., McGuigan, R. & Kretlow, J. (2001). Contemporary Financial Management, 8 Ed. Cincinnati, OH: South-Western College Publishing.
Nationals People’s Action (2010). American Profiteers. Web.
Rivlin. G. (2010). Broke, USA. New York: Harpers Business
Ross, A., Westerfield, W. & Jordan, D. (1998). Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, 4 Ed. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill Publishers.
Uniform Bank Performance Report (n.d.). 2011, Web.
U.S Bank, (2011). U.S Bancorp: Annual financial performance. Web.
Wells Fargo, (2011). Wells Fargo Bank: Annual financial performance. Web.
