Introduction
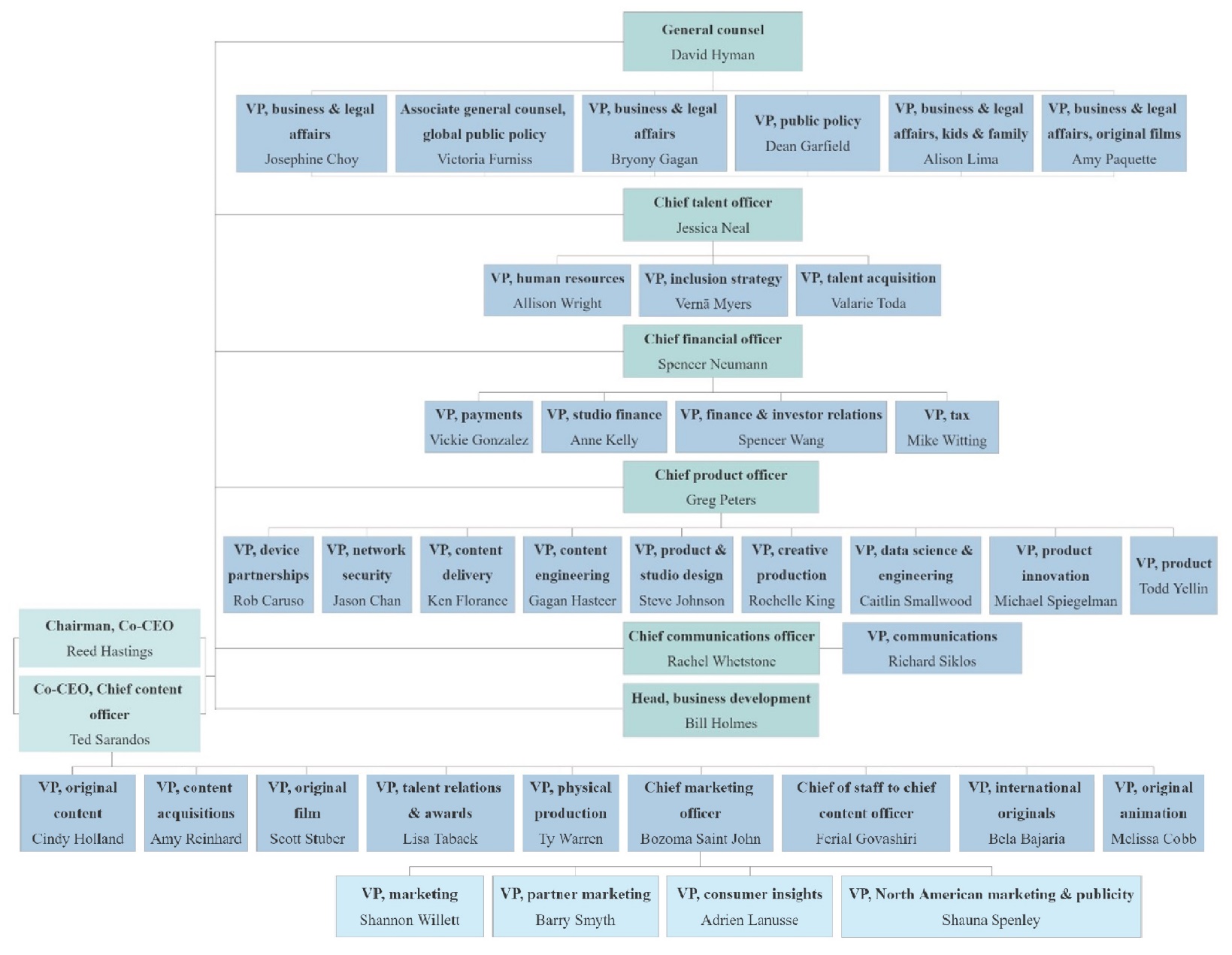
The Netflix Inc. hierarchy has a unitary and organizational structure that prioritizes performance over management. All the company’s key executives directly report to the CEO, excluding micromanagement.
Main offices of Netflix Inc.:
- CEO – executive control.
- Content office – content production.
- General counsel’s office – legal issues, public policy.
- Talent office – recruitment.
- Finance office – financial management.
- Product office – content delivery, security, and product innovation.
- Communications office – customer support, managing social media, blogs.
- Business development – control of sales, search for new clients.
The management chain in Netflix is relatively short, which accelerates communication. Reverse contact in corporate culture is supported by autonomy, avoidance of rules, and efficiency-aiming.
Netflix’s corporate structure operates through Functional, Geographic, and Product divisions. The functional group is responsible for the business plan, finances, and talents. This group affects other offices, coordinating employees’ hire, financial development, and company business strategies. The geographic division is responsible for maintaining competitiveness in the global marketplace, increasing the customer base, preferences, and comparing trends with the company’s strategic plan. The product group is responsible for creating original content, broadcasting, and developing programs and online platforms. It is original content that attracts customers and is an aspect of competition among other companies. Thus, content and product offices are directly connected because the content must be relevant to the global marketplace’s diverse trends, promoted, and eventually streamed through online platforms.
Analyze of the Company Based on Porter’s Five Forces
According to Porter’s five forces, the main threat to Netflix is rivalry among existing competitors, such as Amazon, HBO, Disney, Hulu, and YouTube. Maintaining a top competitor status requires constant technology improvement, a competitive product cost, and the production of original quality content. It is challenging to compete with other companies that offer other subscription products besides video streaming, like Amazon. Netflix chooses to target delivery and gains customers for a larger selection of video content. The recommendation is to consider streaming music as a safety net.
The threat of new entrants is low because it is difficult to grow Netflix’s scale. Access to distribution channels could be advantageous for a new entrant if it has exclusive suppliers. Therefore, the recommendation is to search for providers with more exclusive content than competitors.
The bargaining power of suppliers has a significant impact on the company. The supplier can enter the market themselves, having consumers’ recognition. There is a chance that the supplier will give preference to a competitor. Since streaming companies depend on the suppliers’ quantity and their products’ quality, Netflix has chosen the correct solution of producing original content. The recommendation is a constant search for new cooperation, considering less popular suppliers.
The threat of substitute products appears when the price of an alternative product is lower. In the case of Netflix, torrents, and piracy represent this threat. Pirate content is free, and there are usually no legal issues for online viewers. In this situation, the only solution is to keep working in the chosen direction and keep the strict legal policy. If the company is well protected from cybercrime, there are more chances to protect content.
Consumers can lower the price of products while demanding quality. Companies need to offer the optimal product price to beat consumers’ expectations while not undercutting production quality. Netflix offers a cheap subscription, but the customer is not tied to the company’s other products and can quickly change to a competitor. The advantage is the higher quality of content. Netflix should pay more attention to personalized features and the systematization of content.
Analysis of the Effectiveness of the Leadership Model
Netflix Inc. uses a cost leadership model, which has a competitive advantage by minimizing costs on expenditures. This model implies a broad market orientation by offering low prices through mass production. Using this model, Netflix gains more customers than companies using focus strategies. Netflix also has a strategy of differentiation, with its diversity of products. The disadvantage is the ability of other companies to copy successful innovations. Therefore, Netflix needs to constantly monitor its innovativeness to ensure that it has new idea before the competitor applies the previous one.
The Current Leadership Style in Place at the Company
Netflix has a transformational leadership style characterized by a high level of involvement of the leaders in all company processes and their personal example. This leadership style works through open communication and the search for new ideas, with a minimal emphasis on rules. The purpose of this leadership style is to interest workers in the company’s success. Owing to the director Reed Hastings, the company was able to withstand the technological changes and profit from them.
Alternative Leadership Styles
This leadership style requires the active participation of the leader in both small and global tasks, which has the threat of decreasing the company’s success with the next leader. Netflix’s advantage is the policy of hiring highly competent employees who oversee the company’s progress. Transformational, democratic, and autocratic leadership styles “induce the employees to perform better”, thus “must be promoted in the organizations” (Al Khajeh, 2018, p. 6). Since the replacement of a leader has high risks for a company, a possible solution may be to combine some features of these leadership styles.
What makes a leader effective or ineffective?
From a particular perspective of a leader’s evaluation, there are different ways to determine effectiveness. For a general analysis, attention should be paid to several criteria: quality of execution of tasks, job satisfaction, and subordinates’ professional growth. From a business perspective, an autocratic leader may be more effective than a democratic one, but it is the opposite of a subordinate satisfaction perspective. Evaluating short-term and long-term results might indicate which leadership will be more or less effective.
Sources of Managerial Power
Two primary sources of managerial power are position and personal power. The power of position means “the ability to offer something of value” to others to achieve influence, including rewards, coercion, and legitimacy (Schermerhorn, & Bachrach, 2020, p. 206). The efficient aspect is a reward and coercion, but only a reward has positive power. The power of the person corresponds to personal traits and actions that provide employees’ respect. The quality of the information he provides, the relationship with his subordinates, and the example he sets determine this power. This force has a personal nature and is usually more effective than the first force.
Proposal to the Company
The leadership model can have improvement through reciprocation of some other models’ features. Combining the existing leadership model with the autocratic model can improve the performance effectiveness of the orders “in favor of the organization as per the survey” while “democratic leadership helps in improving the creativity and decision making skills of the employees” (Al Khajeh, 2018, p. 8).
Regarding operational needs, Netflix’s policy is to give employees complete freedom, allowing them to take vacations whenever they need, which gives loyalty and respect to the company. For alignment of operational needs with business strategies, it is crucial to develop the relationship between the mission and its operational resources. Then, to determine the unfulfilled tasks, depending on the targets of each department and the necessary actions to change this situation (such as courses for employees, the right balance between goals).
References
Al Khajeh, E. H. (2018). Impact of leadership styles on organizational performance. Journal of Human Resources Management Research, 2018(2018), 1-10.
Schermerhorn, J. R., Bachrach D. G. (2020). Exploring management. John Wiley & Sons.
