Introduction
The case study selected to demonstrate knowledge of innovation is Dove Chocolate. Dove Chocolate is one of the renowned American chocolate brands manufactured and owned by Mars. The company produces several varieties of products, including ice creams, cakes, milk, and chocolate candies. For Dove, new product development (NPD) is essential for the organization’s future operations and profitability. NPD entails improving existing products or converting new and untried ideas into workable products. NPD primarily focuses on innovating while delivering value. It grabs the market opportunity revolving around customer needs and checking the feasibility of ideologies. The purpose of this research study is to discuss the importance of NPD and innovation for Dove and choose and evaluate one product development model that would help support the process of NPD. In addition, the research also discusses success and failure within NPD and how Dove products will be successful in the marketplace.
The Importance of NPD for the Dove Chocolate Industry
NPD is considered the driving force of businesses and essential for their organic growth. An organization must venture into new products for survival or success due to avid consumer appetite, technology, changing consumer behavior, and strong global competition (Meng, 2022, p. 5). First, consumers change their behavior when their minds are directed, have a clear path for change, and their hearts are motivated. All these conditions must be met for complex changes, including switching brand loyalty and changing habitual shopping patterns. Chocolate makes an interesting case study due to its emotional appeal, substantial international business, and growing consumer demand (Voora et al., 2019, p.3). The product resonates with consumers as it is interrelated with stress-eating, rewards for good behavior, holidays, and romance. The international chocolate market is predicted to grow by 2024, and NPD is expected to spearhead the process, including the cardiovascular health benefits associated with dark chocolate strengthening the demand.
In addition, NPD results in an increased breadth, trust, and transparency of the business. Dove’s in-depth expertise and authority are associated with consumer trust and willingness to engage with the company (Meng, 2022, p. 2). The process of NPD is usually transparent and actively encourages engagement, promoting growth and faster product implementation. Dove performs well in promoting behavioral changes for the rational part of consumer decision-making; it is easy to use and clear. NPD results in increased competition in the organization (Du and Wang, 2018, p.4). For any new development, the initial and utmost essential reason for development is to offer unique value to the customer. The NPD allows trading for new devices, especially if the product is valuable.
Technological advancement has been the cornerstone for NPD to vast industries in the modern business market. For Dove chocolate, NPD is essential in the development of different phases of the product (Sang et al., 2018, p.3). Emerging technologies in confectionary belting coating provide fast coating durations owing to an automatic recipe and controlled process. Similarly, modern technology even coats chocolate surfaces and perfectly coats uneven surfaces (Baxter, 2018, p. 5). Therefore, NPD provides an additional value of new technology and design that directly increases the product value and creates profitability for the firm.
NPD will assist the company in meeting consumers’ needs to the most significant level possible, enhancing brand satisfaction. Dove has a range of products based on tastes, different occasions, and customer needs. The business offers consumers a variety of tastes and colors based on their liking, and by meeting all these needs, the potential for buying the product increases as well as their satisfaction with the brand. Therefore, it can be depicted that the significance of NPD lies in the satisfaction of consumers’ needs. NPD will also provide long-term growth and the business’s survival (Meng, 2022, p. 7). Developing new products will assist the business in increasing market share and maintaining a better competitive market advantage.
Continuous NPD is also linked to advanced research and development capabilities that attract talented teams, promoting the creation of new designs that meet customer needs. NPD, including great and unique design and selling points, can set trends in the chocolate industry and change consumers’ purchasing power and behavior (Thornton et al., 2019, p.6). The prime example is Dove which produces a range of chocolate, some of which have antioxidant that increases cardiovascular health. As a result, the brand is outstanding, and through NPD, it gains more market value.
Stage-Gate Process Model
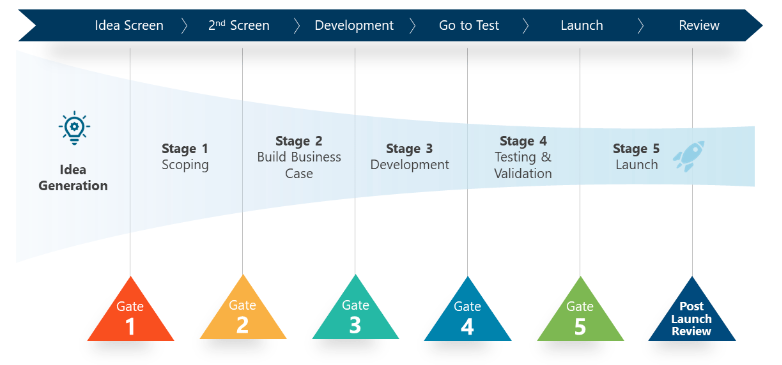
During product development, process improvement, and product improvement, many ideas are explored before proceeding with the most suitable option. The project manager must carefully analyze feasible concepts and ideology and select the most viable option (Cooper and Sommer, 2018, p.1). The stage gate process offers the project managers the tools to scrutinize ideologies for viability before making it to the development stage. The stage or phase-gate process is a technique that assesses the viability of developing a new product or process improvement and business change. The approach is divided into different gates or decision points for analyzing the forecast, risks, resources, and business case to ascertain the best course of action. The stage gate process has five stages: scoping, building a business case, development, testing and validation, and launch (refer to Figure 1).
During idea generation, the process entails finding an idea to pursue. It includes numerous stages depending on the methods employed by the company in search of new ideas and improved process implementation. The process can consist of inter-departmental brainstorming, market research, and feedback from different teams, such as product teams, customers, and suppliers (Cocchi et al., 2021, p.3). Scoping forms the initial phase of the stage gate process, where product viability is analyzed depending on numerous factors like product demand in the market, competitors’ threats, economic and market conditions, and product strengths and weaknesses. In this phase, the organization resorts to tools like PESTEL and SWOT analysis.
Building a business case and plan forms the second and last concept development stage. The phase is divided into four phases: product definition and analysis, business case development and project plan, and feasibility review (Cooper and Sommer, 2018, p.2). The third stage is development, which utilizes plans from the preceding steps to execute the plans that are fleshed out since the product is now determined viable. The development stage can include initial design and development, tests, and prototypes. Marketing plans are proceeding, aligning with the business goals defined for the initiative, and the project timeline is reviewed to ensure the project remains on track. The product is evaluated during the testing and validation phase, and processes are tied to the project. The phase of testing requires near, field, and market testing. The product is launched and ready for use upon passing through all the gates (Cooper, 2022, p.4). The product developer must have a marketing strategy for garnering customers’ interest and attracting demand for the product. Launching considers the volume produced in anticipated product demand, delivery modes, and resolutions to customer complaints.
The model shows a division of labor in the process of NPD for the business, which increases teamwork efficiency and reduces rework. In addition, the process will also assist the business in avoiding the creation of bad products and reducing unnecessary costs, thereby improving management risks and increasing the likelihood of the effective market performance of new products. The stage gate process focuses on the market performance of products and creates mutually exclusive associations amide the NPD processes and their creativity, thereby reducing workers’ enthusiasm.
Success and Failure
Product Success
The success of NPD depends on the effort of the team. While designers are accountable for the product’s usability, utility, and user experience, many factors contribute to the success and failure of NPD, some of which are outside the designer’s direct control. Some of the factors for NPD success include knowledge management, market orientation, NPD process, NPD speed, strategies, teams, technology, and top management support (Hemonnet‐Goujot et al., 2019, p.6). Support by top management is critical to the success of the business project as the support guarantees resource allocations and project prioritization. In an organization, the support is determined by the decision-makers importance and the company structure associated with NPD (Ind and Iglesias, 2022, p. 2). The administration’s attitude determines the strength of the support given to the project being developed, and its direct influence on NPD includes human resource, financial, and technological involvement.
Market orientation entails the organization’s philosophy focused on meeting and discovering the desires and needs of customers through product mix. The company philosophy must be in an excellent position to impact NPD through user and market research aiming to develop high-quality products (Cooper, 2019, p.4). The technology used for creating and delivering the product must be suitable for the market to realize success (Zhang et al., 2021, p.3). Another important factor for NPD success is knowledge management, which aids in the provision of resources to support product development. Refining the design process to maximize speed and maintain or protect the user experience is an important activity that the designer remits (Baxter, 2018, p. 5). Product development must take the shortest time possible when the demand and market are still viable as the industry changes rapidly with consumers’ purchasing behavior.
Dove Chocolate Product Failure
Dove products fail for various reasons, including lack of product originality, inefficient timing, poor planning and execution of marketing plan, product flaws, wrong market research, incorrect pricing, and weak launch. If Dove’s chocolate product lacks originality, it has the potential to fall behind similar products existing in the market. To avoid failure, new chocolate products are required to be appealing and different. Timing is also a determinant factor for the success and failure of a Dove product developed. Having wrong timing makes the developed product not get the attention it needs for survival in the market, which fails. Poor planning guarantees the failure of the product because the strategies involved will not produce the product that meets consumers’ needs, and the product may stick around for a short time.
In addition, NPD failure can be a result of product flaws. When consumers realize and have personal experience with a flawed chocolate product, they immediately gain a negative opinion about it, which affects the demand and lower profitability. Product flaws can be attributed to wrong market research that leads to an unclear understanding of consumer needs. Incorrect pricing also makes the chocolate product impossible to reach the average consumer. A weak launch can make the product not get early feedback, which creates opportunities for product strengthening.
How Dove Can Avoid Failure of NPD
To ensure the success of the NPD, it will be important for Dove to mitigate all the causes of potential failure. The company will ensure all the decision-makers provide sufficient support to NPD, including financial and technical support. Dove will also consider factors such as consumers’ needs, design philosophy, competitors, product pricing, and external market conditions in its design process. The product’s pricing will be done so that it is strategically positioned to target customers, and the launching is strong enough to attract more customers and exploit the feedback for opportunities.
Conclusion
The paper provides a discussion and an evaluation of the importance of NPD to Dove Chocolate Company. It is depicted that NPD will add value to Dove products and make the new products marketing points for the business. Through NPD, the company will be able to meet consumer needs and make profits that result in its growth, create a good business environment, and use the new products for setting trends. To ensure that NPD is successful, the organization employs the stage gate process model that comprises five phases that assess the viability of the new ideas and improvement. The study ends with an explanation regarding the failure and success of NPD and provides potential solutions that Dove business can employ to avoid NPD failure.
Reference List
Baxter, M., 2018. Product design. CRC press. Web.
Cocchi, N., Dosi, C. and Vignoli, M., 2021. The hybrid model matrix enhances stage-gate with design thinking, lean start-up, and agile: managers can use the hybrid model matrix to decide when to use design thinking, lean start-up, or agile with stage-gate to boost new product development. Research-Technology Management, 64(5), pp.18-30. Web.
Cooper, R.G. and Sommer, A.F., 2018. Agile–Stage-Gate for manufacturers: changing the way new products are developed by integrating agile project management methods into a stage-gate system offers both opportunities and challenges. Research-Technology Management, 61(2), pp.17-26.
Cooper, R.G., 2019. The drivers of success in new-product development. Industrial Marketing Management, 76, pp.36-47. Web.
Cooper, R.G., 2022. The 5th generation Stage-Gate idea-to-launch process. IEEE Engineering Management Review. Web.
Du, J. and Wang, Y., 2018. The relationship between brand positioning and packaging color of chocolate. In 4th International Conference on Arts, Design and Contemporary Education (ICADCE 2018) (pp. 572-574). Atlantis Press. Web.
Hemonnet‐Goujot, A., Manceau, D. and Abecassis‐Moedas, C., 2019. Drivers and pathways of NPD success in the marketing–external design relationship. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 36(2), pp.196-223. Web.
Ind, N. and Iglesias, O., 2022. Communicating and demonstrating conscience. In In Good Conscience (pp. 125-143). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. Web.
Meng, X., 2022. The analysis of customer behavior across cultures is based on the marketing activities of Dove Chocolate. Academic Journal of Business & Management, 4(4). Web.
Sang, H., Xue, F. and Zhao, J., 2018. What happens when satisfied customers need variety? –Effects of purchase decision involvement and product category on Chinese consumers’ brand-switching behavior. Journal of International Consumer Marketing, 30(3), pp.148-157. Web.
Thornton, S.C., Henneberg, S.C., Leischnig, A. and Naudé, P., 2019. It’s in the mix: How firms configure resource mobilization for new product success. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 36(4), pp.513-531. Web.
Voora, V., Bermúdez, S. and Larrea, C., 2019. Global market report: cocoa (p. 12). Winnipeg, MB, Canada: International Institute for Sustainable Development.
Zhang, H., Zhang, X. and Song, M., 2021. Deploying AI for new product development success: by embracing and incorporating AI in all stages of NPD, companies can increase their success rate of NPD projects. Research-Technology Management, 64(5), pp.50-57. Web.
