Executive Summary
Established in 2004, Talabat is a global “q-commerce” online food and grocery ordering business. With a commanding 55% market share, it is regarded as the biggest and most well-known online meal ordering business in the area. The Talabat platform focuses, at its core, on connecting vendors such as restaurants and shops with consumers. This paper discusses in-depth the internal and external stakeholders that have an influence or presence in the Talabat ecosystem as well as discussions on their management. The project environment is then carefully dissected by applying a careful PESTEL analysis to identify a range of potential external factors. The general business environment and potential for the company and industry are then discussed. As a q-commerce company, Talabat has a significant opportunity for growth as the sector is seeing unprecedented increase in popularity and market adoption currently. As social shifts such as urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and work-from-home lifestyles expand, the trend will continue to be the core of modern business at the local level. Talabat is the forefront of the industry in food-delivery which is the largest sector in the q-commerce environment. Finally, the impact of CSR is presented. First the definitions and basic models of CSR are introduced. That is then applied to Talabat, discussing some of the company’s notable activities for community support and sustainability. The company’s position on CSR is outlined and possibilities of government public-private cooperate are proposed in terms of policy and initiatives. The report wraps up with a conclusion outlining the contribution of this research to the general knowledge in the industry.
Introduction
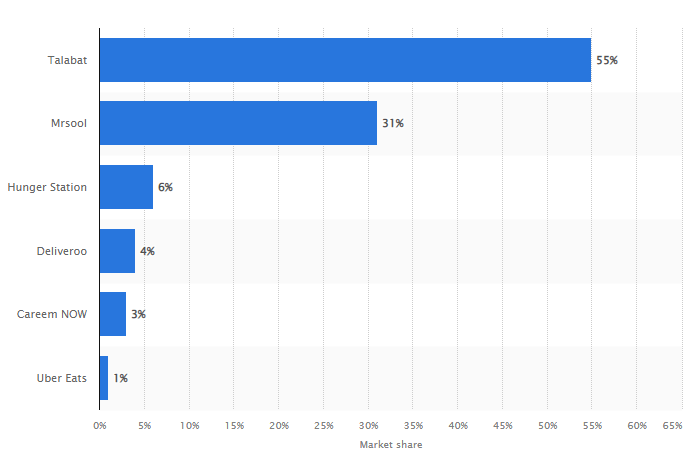
Talabat is a multinational ‘q-commerce’ online food and grocery ordering company founded in 2004 Kuwait. As of 2021, it operates in virtually all countries of the MENA region, including Qatar. The company is currently owned by the multinational German conglomerate Delivery Hero, serving as its subsidiary in the Middle East (Talabat, 2022). It is considered to be the largest and most popular online food ordering enterprise in the region with an overwhelming 55% market share (Statista Research Department, 2022).
The primary goal of the Talabat platform is to link customers and merchants, including eateries and retail establishments. Talabat offers a sophisticated technological platform which contains large databases of vendors and consumers, offering appropriate choices to customers based on location. Talabat also hires delivery persons as part of its staff, who operate typically as independent workers partnering with Talabat for revenue. Vendors have the choice of delivering the products themselves or using Talabat couriers who receive information regarding where to pick up the order and location of delivery. In the final leg, the customer receives the product, with the options to having pre-paid when ordering or paying upon receival.
Talabat itself bears the responsibility of managing the online platform, talking online orders, managing logistics and transactions, and perfecting algorithms that offer the best matching services between consumers and vendors based on consumer needs or preferences. It is an overall beneficial value proposition for all participants involved. Customers receive the factor of choice, convenience and speed along with various features such as tracking orders and ordering for a specific delivery time. The restaurants receive access to a wider customer base, which particularly in the context of the post-pandemic era is significant as in-person dining has declined significantly after 2019. This type of model also helps to manage efficiencies and operational expenses, as Talabat offers data analysis along with feedback from customers. In the context of a gig economy, Talabat serves as an additional source of money for delivery persons, particularly those in low-skill labour looking for income. Finally, Talabat has a consistent revenue stream by taking a small commission on each order as well as delivery charges and advertising income on its platform (Jain, 2020).

Project Stakeholders
Internal Stakeholders
- Talabat CEO Tomaso Rodriguez – Rodriguez is a former executive at Talabat’s parent company Delivery Grab and was appointed CEO in 2019. The manager has extensive experience around the world in the space of q-commerce in food delivery and has led Talabat to maintain a leading position across MENA despite growing competition. He is critical to the company’s continued growth, diversification, and innovation to continue providing high quality service to customers and vendors with more available options and features.
- Board members – the Talabat board is made up of experienced managers across the industry, they work with the CEO and other executives to drive the company’s strategy and participate in vital decision-making at the corporate level.
- Talabat employees – the employees at Talabat are a strong part of the team, knowing they are working in a technology company first and only then food and service business. The business requires diverse teams across a variety of disciplines to maintain, market, and develop the platform across the various markets in the MENA region. The atmosphere in the company is open and forward-thinking, maintaining a European approach to business while being predominantly Middle Eastern.
- Delivery persons – although serving as independent contractors, delivery persons working for Talabat are a critical core of the business and serve as a key stakeholder. Although it is low-cost labor and this stakeholder group is not responsible for any decision-making, they must be kept informed and satisfied, with viable working conditions and compensation offered, because without the delivery component, the platform will collapse. Furthermore, the business is consistently competing with other q-commerce firms in the same or other industries for the limited labor power.
External Stakeholders
- Qatar government – the local government provides a business climate which allows for both, small businesses, and vendors as well as online platforms such as Talabat to thrive. There are often incentives through policy for the digitalization of the economy, which the online platform is successfully doing, creating an effective structure and attracting new jobs and entrepreneurship.
- Social Media – Success of online platforms cannot be achieved without an extensive social media presence, allowing for greater exposure to consumers based on location and interests as well as general marketing and content creation. Social media platforms have been vital to Talabat’s growth, generating significant followership.
- Community/population – Talabat’s business model allows to connect various stakeholders within the respective local communities. The platform is designed to bring value added to everyone, while being profitable. Talabat does not seek to take much from the businesses nor raise prices for consumers, it is an accessible method of cooperation within the community.
- Restaurants – the restaurants are the primary business vendors with which Talabat cooperates as the majority of deliveries are food. Restaurants are influential stakeholders because while joining Talabat would be beneficial to them, they also hold an advantage as without restaurants the company would not exist. It is important for Talabat to maintain good partner relationships with these businesses to provide the best offers available.
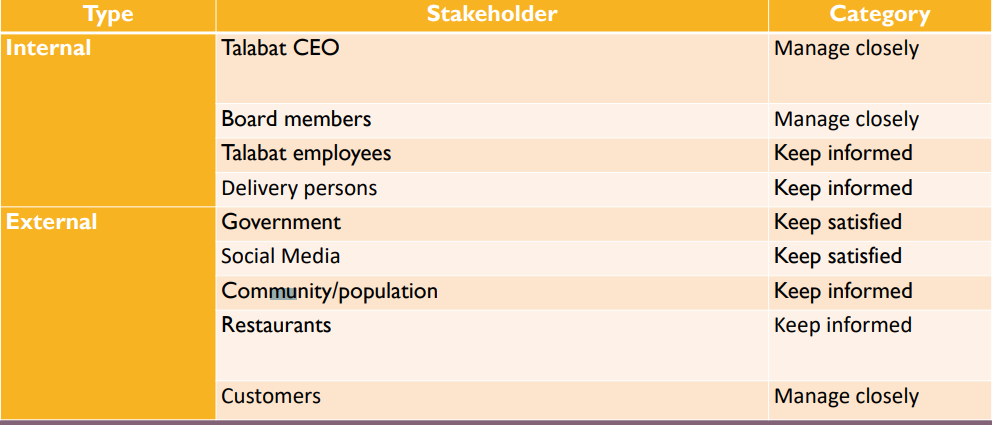
- Customers – Talabat is of course primarily a b2c business, as the consumers are their direct clients. The customers download the Talabat app and register in order to browse vendors and choices available. It is based on consumer orders, through fees, that the company attains its primary revenue. Consumers are the most vital external stakeholder, that should be managed closely to promote satisfaction and retention on the platform in the long-term, as the model strongly depends on consistent users.
Project Environment
PESTEL Analysis
Political Factors
Political factors are a strong influencing factor for Talabat in Qatar. The Ministry of Commerce and Industry strongly regulates businesses, particularly e-commerce and delivery companies which use online platforms to operate. There are a range of guidelines and regulations aimed at consumer protection, service offering, data management, and even the pricing of goods and services, including the fees and percentages that Talabat can levy from its vendors for the service and delivery, capped at 19% from total order value (The Peninsula, 2022). There are also regulations to be considered in regard to the gig economy as Talabat hires delivery persons as independent contractors. The Ministry must approve any major shifts in the business functions of the company and while the government is generally friendly to business, it is expected that regulations are followed. Taxation is also a political issue, with corporate taxable income subject to a flat CIT rate of 10%. Also, international politics may play a role, as Qatar has faced political and economic isolation before from the other members of the GCC, with threats of potential sanctions for its geopolitical activities, that may threaten operations of international firms such as Talabat from operating in the country.
Economic Factors
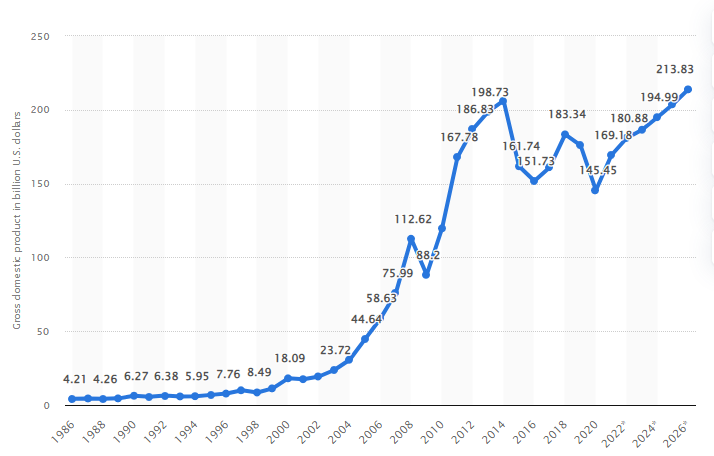
The economic environment in Qatar is positive, having rebounded after the pandemic and flourishing for business. With high energy prices, Qatar which receives the majority of its revenue from hydrocarbon exports, is seeing significant budget surplus, which translates to strong subsidies and social support for the population. The GDP of Qatar is expected to continue increasing in the next decade, particularly as the country increases energy exports, reaching a total of $213b from the current $169b by 2026 (Statista, 2022). Inflation in Qatar has been steadily low, although prices are expected to increase on global commodities such as food due to various crises. Unemployment in the country is similarly low and various industries are expanding providing job opportunities. Individuals are expected to have greater disposable income which is beneficial for q-commerce services such as Talabat.
Social Factors
The Qatar population is becoming exceedingly modern and strong participants in the digital economy. As mentioned earlier, greater disposable income combined with an 85% Internet penetration rate in Qatar is resulting in a population that is actively embracing new digital trends, particularly seeking to emulate some of Western consumer behaviours. The population is actively engaged online and on social media, and there is evident growth in the e-commerce sector, expected to nearly triple by 2022 to QAR 12 billion (US $3.2 billion) (International Trade Administration, 2020). Furthermore, the q-commerce sector is benefiting from the adoption of e-commerce, achieving the last-mile delivery to consumers on a range of products. The market in the MENA region is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 17% over the next decade, with food and grocery delivery continuing to be the dominating sectors (Qatar Tribune, 2021). Even as pandemic restrictions are lifted, Qatar consumers have embraced the convenience and variety of choice factors for the business model of Talabat.
Technology Factors
Talabat is a technology company primarily, so it heavily relies on various technological elements to function. It must upkeep its servers to maintain consistent functionality. It must also continuously develop and support its software as the primary aspect of consumer interaction, making functionality easy and intuitive to place orders. The company has to develop algorithms that can utilize user data to provide them the best options in their respective locations. Furthermore, with the growth of robotics, the company is investing into future possibilities of autonomous delivery, already testing both drones and ground based carriers.
Environmental Factors
A major environmental factor for a company such as Talabat to consider is waste. Due to the rapid and temporary dining aspects of its service delivery, there is a lot of waste ranging from plastic bags to food containers and plastic bottles. While the burden does not fall on Talabat along since the service essentially delivers the food, it has a role to play due to the scale of the business. Efforts are made, as will be discussed in the CSR section to limit environmental impacts. Overall, climate change does have an impact on the functionality of the business, as climate directly affects both food prices and availability. Furthermore, the practical aspects of delivery by humans may be challenging during some seasons with the increasing temperatures in the country.
Legal Factors
Talabat competes with various other brands in the region and Qatar. It must take legal steps to protect its trademark and patent its technological platform. While the business model of an online delivery platform itself is not unique, various aspects of the platform such as design, algorithms, and other unique elements can be trademarked. The company also faces various legal responsibilities while operating in Qatar such as providing appropriate wages and safe working conditions for its workers. The company also has legal contractual obligations with the businesses that it engages with and consumer protections that must be followed.
External Environment
Just as e-commerce arose with the advent of the Internet, allowing to shop and order anything online, q-commerce, otherwise known as ‘quick commerce’, is the next iteration of the modern economy. It is a convenient method of growing business channels that specialize in on-demand and rapid delivery, companies which typically deliver products in under an hour on average time. Q-commerce is the latest trend in the internet economy, particularly as the COVID-19 pandemic forced lockdowns around the world, instantly popularizing consumer behaviours such as on-demand instant delivery, willing to pay the higher prices for the convenience and speed. The trend will remain crucial to contemporary local business as social changes including urbanization, growing disposable incomes, and work-from-home lifestyles spread (Bommireddipalli, 2022). Most regions have developed similar services, with Talabat being the leading hub in the Middle East. Talabat primarily specializes in fresh food delivery, but as of 2022, the company’s couriers in most major cities can deliver groceries, flowers, and pharmaceutical products.
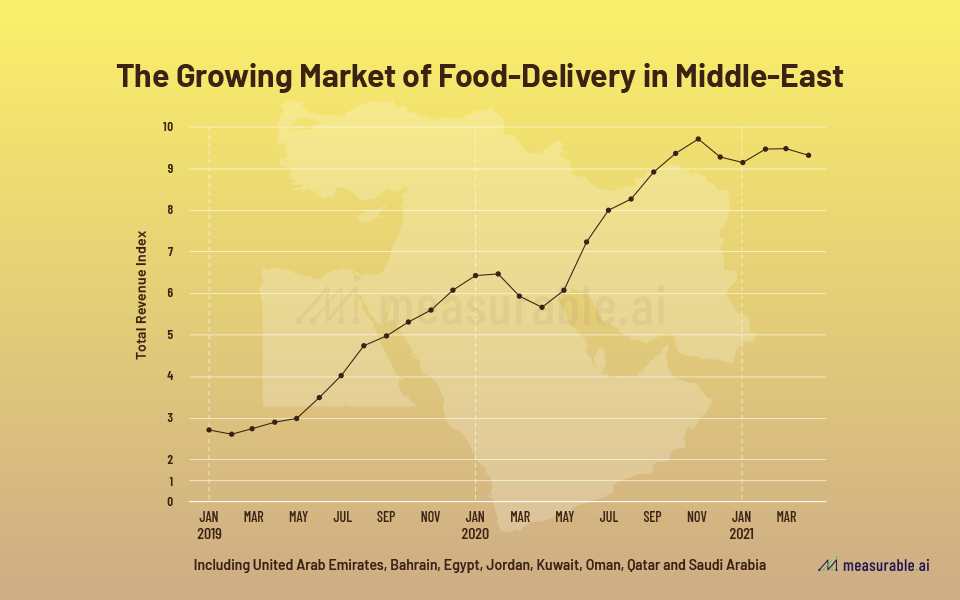
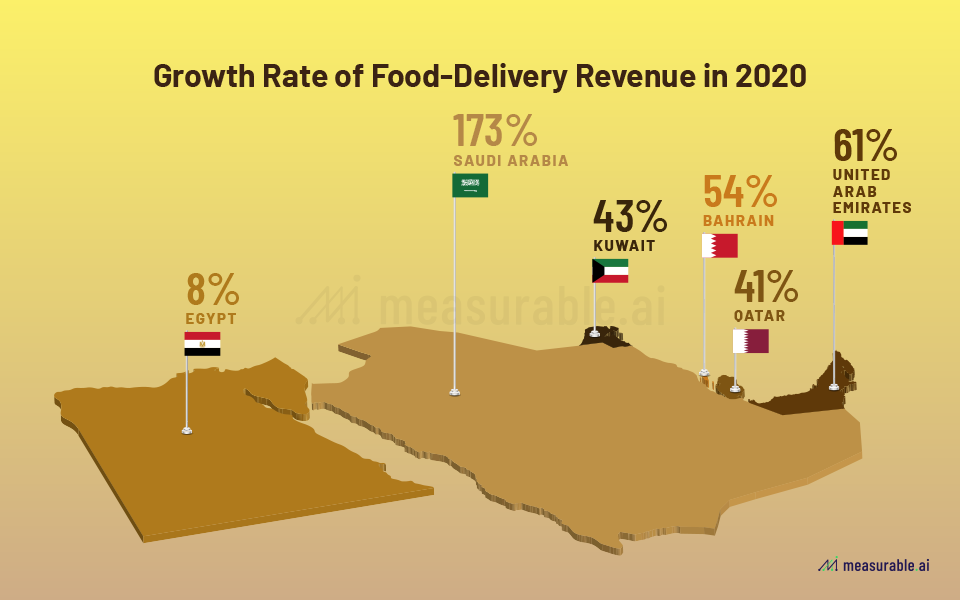
As with most regions in the world, the COVID-19 pandemic has brought the rise of the food delivery market in the Middle East, nearly doubling in revenue in 2020 seen in the chart above. The MENA market including in Qatar has been untapped in terms of food delivery penetration and has seen an extraordinary rate of growth with the pandemic. As seen in the graphic below, the highly wealthy and tourist-based countries of Saudi Arabia and UAE have seen the biggest growth, while Qatar remains at 41%, indicating that there is likely some potential. Food delivery and q-commerce are generally more expensive than traditional market and grocery store food purchasing, but Qatar is a wealthy state as well. Therefore, it may a wide range of considerations of why higher rates are not yet seen ranging from slow cultural penetration to more limited marketing campaigns in the country compared to its neighbours. However, the general economic climate as well as socio-cultural attitudes which seek to emulate Western lifestyles are promising for the growth of digital platforms such as Talabat in the food delivery space.
The q-commerce industry in Qatar had experienced a critical growth moment as a result of the pandemic as well. Talabat in Qatar started not only working with restaurants but created an online market for quick delivery of grocery and essentials. Talabat mart is a fully virtual enterprise in retail, one of the first of its kind in the country, allowing the concept to focus on rapid order fulfilment, efficiency, and affordability (Gulf Times, 2020). The Qatar economy and government are creating stimulating environments for such projects. For example, the Qatar Science and Technology Park funded by the government has an incubator centre for innovative start-ups and programs in the field of technology. One innovative start-up Airlift QSTP has partnered with Talabat to begin pilot programs for autonomous delivery by drones and self-driving vehicles in Doha (Afreno, 2021). The Qatar Foundation as funded by the government is seeking to support a business environment where companies can enter to enhance the lives of residents, with solutions like Talabat being one of them.
Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a concept becoming increasingly adopted across the business world at all levels as a form of self-regulation and internal policies that are meant to reflect and demonstrate a company’s values. The primary purpose of CSR is typically accountability and commitment to its customers and the community where it operates through various measures such as social justice, environmental sustainability, support of underprivileged groups, and others. While CSR is crucial to brand perception and public reputation, CSR measures are meant to be more than just PR stunts but practices that seek to improve communities, the economy, and environment (Reckman, 2022),
CSR has become widespread internationally, and has been codified by the International Organization for Standardization in a framework known as ISO26000. It 7 core elements to organizational governance that companies can employ to maintain a holistic approach to CSR. As mentioned, CSR goes beyond a public relations activity such as giving back to the community (although it is important and community involvement is one of the core subjects), it is meant to penetrate organizational operations and values via aspects such as labour practices, environmental sustainability approaches, human rights, addressing key consumer issues, and just fair operating practices (ISO, 2020).
As a modern flourishing company, Talabat like many tech firms, takes CSR seriously. It has adopted many practices and initiatives that are meant to benefit its workers, the community, and the environment. Although the company works in a high-pressure environment, it offers exceedingly fair labour practices and compensation, even for the low-cost labour of delivery persons. It is a company which seeks to espouse positive values and support for the global community and environment. Two key CSR initiatives stand out in recent years. First, during the pandemic, when businesses were struggling and the economy shrinking, Talabat shifted its model slightly. It allowed for vendors that it works with to receive pay-outs from their orders every three days instead of biweekly or monthly as it has done before. Despite potential risks due to potential customer returns or complaints, Talabat’s decision was a major contributing factor allowing to generate cash flow for struggling businesses and continue day-to-day operations (Nabeela, 2021). The company did this voluntarily along with supporting the small businesses in the community the best it could. The managing director if Talabat Qatar indicated that it was the correct move in a mutually beneficial environment, “We urge all big players in their respective industries to truly consider what is best for their ecosystem, and proactively introduce sustainable changes to empower those within it” (Nabeela, 2021, para. 4).
Another CSR measure that Talabat has introduced recently is meant to address the environmental issue of plastic waste and carbon footprint. The company has shifted its operations in Qatar to sustainable plant-based biodegradable packaging. For now, being a limited pilot project, but the company will provide this packaging for its vendors to use. It reflects well on the environment, as well as addresses consumer concerns, as more than 88% in Qatar have voiced the desire to see sustainable delivery systems (AlSharif, 2021). Given that Talabat operates in multiple countries, as well as being owned by another multicontinental conglomerate, it is working with its partners to develop the initiative across markets around the world in order to achieve the economies of scale with both, producing the packaging as well as the total environmental impact it will have. Given the available information, in the context of the CSR stance matrix, Talabat can be placed at the level of forum for stakeholder interaction. They are proactive, maintaining a close partnership with stakeholders, champion CSR through leadership and organization-wide policies, and value sustainability at the core.
The Qatar government promotes and supports CSR activities from firms, particularly in the areas of sustainability and community outreach, with a clear strategy for the role of the business sector outlined (Qatar Chamber, 2022). It is not known what the government reaction was to Talabat’s CSR activities, but it is likely they are welcomed. Given the scale and market penetration of Talabat, the government can work with the company and perhaps other firms in the sector to promote such activities. Particularly in the initiative to reduce plastic waster and introducing biodegradable containers, a private-public partnership can be developed via policies which subsidize firms that transition to such initiatives. That will encourage companies to find innovative approaches to sustainability with both practical applications such as this or investing into future technologies such as autonomous delivery machines running on renewable energies. If the Qatar government pursues this path, firms like Talabat will be able to extensively enhance their CSR impacts.
Conclusion
Talabat is a multi-national innovative company in the food and grocery delivery industry that is driving the rapid adoption of the q-commerce model in Qatar. Having the benefits of ease of use, convenience, and technological platform to connect businesses with consumers, Talabat is the future of consumer technology solutions in the modern marketplace. Due to the close community ties that it has, Talabat adapts to local cultures as well as utilizes its business to aid local businesses and environments through coordinated CSR efforts, setting small but impactful trends in regard to its sector. This report examines the origin, business model, stakeholders, external environment, and CSR around Talabat, providing key insights and recommendations in relation to the business in its respective industry. Through an examination of past and current successes of innovative companies such as Talabat, future progress can be made to achieve optimal quality and level of services and options to the consumers.
Reference List
Afreno. (2021) Qatar economy adapts to COVID through innovative delivery bots. Web.
AlSharif, F. (2021) Talabat to introduce 100% plant-based packaging in Qatar. DohaNews [online], Web.
Bommireddipalli, R. T. (2022) What’s next for q-commerce: The golden child of e-commerce. Forbes [online], Web.
Gulf Times. (2020) Talabat launches q-commerce store. Web.
Jain, A. (2020) How Talabat works – business and revenue model explained. Oyelabs[online] Web.
International Trade Administration. (2020) Qatar e-commerce opportunities. Web.
Nabeela. (2021) Talabat Qatar announces cash flow initiative for vendors. IloveQatar [online] Web.
Reckmann, N. (2022) What is corporate social responsibility. Business News Daily [online], Web.
Qatar Chamber. (2022) Corporate social responsibility. Web.
Qatar Tribune. (2022) Valuation of q-commerce market in Mena region may reach $47 bn by 2030: Report. Web.
Statista. (2022) Qatar: Gross domestic product (GDP) in current prices from 1986 to 2026. Web.
Statista Research Department. (2022) Revenue share of food delivery market in the Middle East in 2020, by company. Web.
Talabat. (2022) Our story. Web.
The Peninsula. (2022) Ministry of Commerce calls on delivery companies to comply with price of goods and services. Web.
Yang, J. (2021) The rise of food delivery market in the Middle East. Measurable.ai [online] Web.
