Introduction
The Internet is an integral part of contemporary culture. Social networks, the development of which has occurred rapidly, appeared in their depths. Social networks have revealed themselves to be a unique and sustainable cultural phenomenon, and with their increasing popularity in society today, they are influencing it extensively. The more functions a socials offer, the more time a person is willing to devote to them. An Internet page is a small island of virtual space belonging only to one person. Filling it with favorite music, lyrics, pictures, and videos is comparable to inviting other people into one’s inner world while simultaneously being at a safe distance. Despite its advantages, virtual reality is always complete with dangers and mysteries. Generally, the phenomenon of social networks is ambiguous though it has a significant role in modern society.
Media and Socialization
It is evident that in the modern era of information, a person needs the familiar feeling of the group. City life separates people, the pace accelerates, individuals move to other cities, and the Internet allows one to be in touch with close people. Wong claims that “looking at the statistics, one can notice that now 2 billion people are connected to social networks, and by the way, it is practically a little bit less than 1/3 of the world’s population” (256). It means that they have become a necessary means of existence. Being online means being alive, having an instant answer, and being available for communication 24 hours a day, seven days a week. The offline status is perceived as the absence of a person in society and certain helplessness because of the lack of communication. It may be remarked that social networks are more credible than forums and blogs. Thus, the benefits they provide and their indispensability are indisputable.
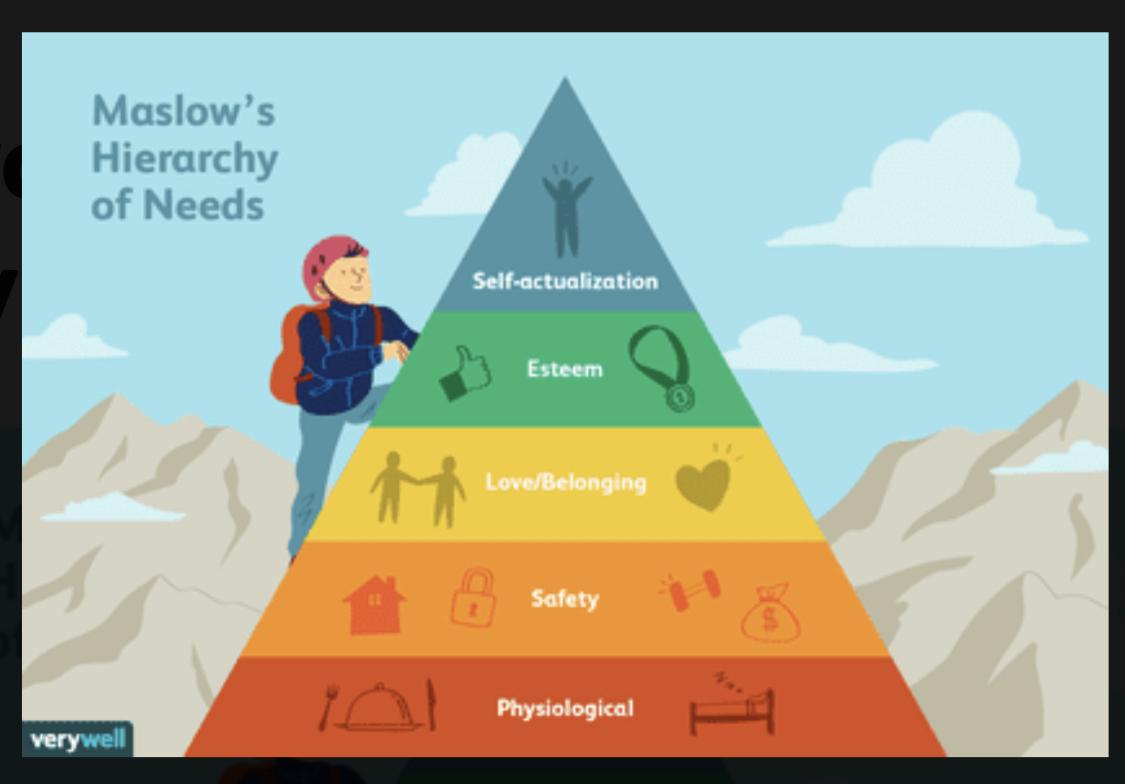
Remarkably, communication in social networks has long been a particular communication genre. For a short time, it has emerged as an independent system of rules of behavior and culture, which all the active participants in this dialogue, to varying degrees, relate. According to Riehm “socials are perceived as a necessity, without which it is challenging to exist” (1268). This argument can be supported by numerous theories and concepts. For example, considering social networks in A. Maslow’s theory of human needs, they satisfy the human condition to belong to a social group (Seong). This demand is the highest level for most people, and social networks act as the most straightforward way to satisfy it. Therefore, they act as a platform for self-expression, especially for young people, which raises their needs to a higher level.
The Impact of social Media on Young Generation
The entire basic life of young people is spent exploring social network news feeds, watching videos of favorite bloggers, and constantly communicating with friends worldwide. Bloggers are idols and authorities for young people of different ages, from very young to older ones. Most viewers often do not filter the information’s value and whether it is worth trusting. Keles et al., claim that as tempting as the benefits of social media may be, it impacts the pastime of young people and their socialization process and psyche (80). The fact that children who have just embarked on the path of personality formation spend all their free time in the virtual world suggests that many of them may not acquire the necessary social skills in the future.
Safety issues pose the greatest danger among the long list of disadvantages of social media. The virtual world is different from the real one, which only complicates the ability to protect oneself (Hinton). Rejecting television as mass culture, young people do not realize that the Internet can be an even greater evil because there is minimal control over the content of Internet resources. Kahne and Bowyer state that “by acting subconsciously, the social network corrupts and zombifies young people” (473). Violence, cruelty, and the denial of moral norms and foundations, this is only a tiny part of what they contain. Radical, provocative, and extremist ideas are now actively spreading on the expanses of the Internet, and most often, in a hidden form.
Still, the same idols of young people can serve these ideas. According to Fondevila and Francesc “over the past 10-15 years, extremist movements and groups have gone beyond the regional territorial outlines to the national and global levels” (1508). However, the introduction of laws does not eradicate extremist activity and only forces groups to adapt to the changing conditions of the political and legal space. It means that social media carry numerous risks, and preventing them is everyone’s responsibility.

Conclusion
Thus, it can be concluded that social networks act as the basis of modern civilization, in particular the culture of young people, which contributes to meeting the social needs of the individual. Active communication in social networks develops intelligence and its interrelationship with the other components of the psychological culture of the personality of Internet users. Thus, the intensive communication experience, even in a specific environment, can be considered a source of enhancement of psychological culture. Nevertheless, social networks have become a unique, open platform for spreading extremist views. Young people are most vulnerable to extremist ideas as a mentally unstable group who spend most of their time on the Internet, communicating with friends and constantly encountering various kinds of information. Social media are beneficial, but it is essential to comprehend how to use them to avoid possible risks.
Works Cited
Fondevila, Gascón, and Joan Francesc. “Social Media Influence on Youngsters Behavior.” Sustainability, vol.12, no. 4, 2020, pp. 1506-1509.
Hinton, Bill. “Cyber Hacker Red-Stock.” GettyImages, 2019, Web.
Kahne, Joseph, and Benjamin Bowyer. “The Political Significance of Social Media Activity and Social Networks.” Political Communication, vol. 35, no.3, 2018, pp. 470-493.
Keles, Betul, Niall McCrae, and Annmarie Grealish. “A Systematic Review: The Influence of Social Media on Depression, Anxiety and Psychological Distress in Adolescents.” International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, vol.25, no.1, 2020, pp. 79-93.
Riehm, Kira. “Associations between Time Spent Using Social Media and Internalizing and Externalizing pProblems among US Youth.” JAMA psychiatry, vol. 76, no. 12, 2019, pp. 1266-1273.
Seong, Joshua. “Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.” Behavioural Psychology, Verywellmind, 2022, Web.
Wong, Adrian. “The Use of Social Media and Online Communications in Times of Pandemic COVID-19.” Journal of the Intensive Care Society, vol. 22, no. 3, 2021, pp. 255-260.
