Introduction
PepsiCo is a multinational organization based in North America that deals with food, snack, and beverage. It is the second-largest food and beverage company in the world behind Nestlé. PepsiCo was established in 1965 through the merger of Pepsi-Cola and Frito-Lay (Kelloway & Miller, 2019). Its products are beverage brands such as Pepsi, Mountain Dew, Gatorade, Tropicana, and Lipton. In addition, the organization produces snack brands such as Frito-Lay, Quaker Oats, and Doritos. The company has a strong presence in more than 200 countries across the globe (Kelloway & Miller, 2019). It is committed to offering sustainable products, creating a healthier future, and making a positive difference in the world. Its initiatives and investments focus on nutrition, water, packaging, and climate change. Through its sustainability goals, PepsiCo seeks to reduce its carbon footprint, create healthier products and improve access to clean water.
Problem Statement
PepsiCo has been facing issues with the quality of its products. This is especially true of its drinks, which have been criticized for having much sugar, artificial flavors, and other unhealthy ingredients (Bishnoi & Poonam, 2020). PepsiCo has been accused of using cheap ingredients and preservatives in its products, which can change their taste. Many consumers have complained about the taste and quality of PepsiCo’s products, from its flagship cola to its various snacks. The company has been criticized for using high fructose corn syrup, which is considered unhealthy and linked to obesity (Abu-Reidah, 2020). Additionally, artificial colors and flavorings have been a source of concern for many consumers. Therefore, the question to be answered is: which initiatives can PepsiCo introduce to ensure the consistent quality of its products and increase customer satisfaction?
As-Is Condition
Current Condition
PepsiCo’s supply chain process has fallen short regarding ensuring product quality. This is because the supply chain process is focused on efficiency and cost-effectiveness rather than product quality (Purkayastha & Rao, 2017). As a result, PepsiCo has been unable to produce products that meet customer expectations consistently. Furthermore, the supply chain process fails to provide adequate oversight of subcontractors, leading to issues with quality control. This has led to customer dissatisfaction, as PepsiCo products do not always meet the quality standards that customers expect (Purkayastha & Rao, 2017). For example, the company has failed to interact closely with its suppliers to ensure they provide quality raw materials at affordable prices. Therefore, PepsiCo’s supply chain is not stakeholder oriented because it has failed to ensure that customers and vendors are satisfied.
Process
The process flow chart is current PepsiCo’s supply chain process. As shown in figure 1, PepsiCo’s supply chain process begins with the procurement of raw materials. The materials used are sourced from suppliers located across the globe (Li et al., 2020). After the raw materials are procured, they are sent to factories and manufacturing plants to be processed and packaged into consumable goods. From the factories, the goods are distributed to warehouses and distributors. The distributors then deliver the goods to supermarkets, convenience stores, and other global retail outlets (Li et al., 2020). Finally, the goods are purchased by consumers from different retail outlets. PepsiCo’s supply chain is designed to ensure quick and efficient delivery of goods from the production line to the consumer. The organization has a robust system for tracking and monitoring the progress of the goods throughout the supply chain.
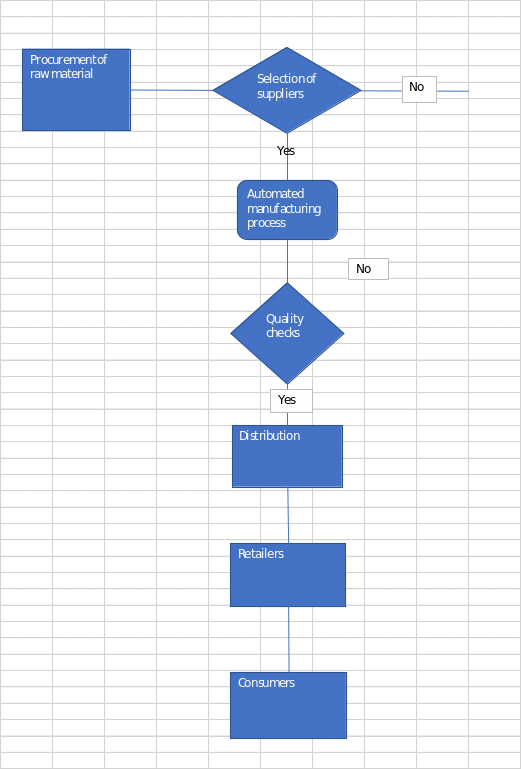
Project
The project is dedicated to ensuring that PepsiCo produces quality products by ensuring its safe and secure supply chain. This involves putting quality control measures in place at every step of the supply chain, from getting the raw materials to making the product to distributing and delivering it (Schermerhorn et al., 2020). This is about ensuring that the materials come from trustworthy sources, that the production process is closely watched, and that the finished product is tested for quality. PepsiCo should work with trusted third-party organizations to audit the supply chain process and make sure that standards are being met (Schermerhorn et al., 2020). Therefore, they are supposed to use high-tech tools to track and keep an eye on the supply chain process and ensure that quality standards are always met.
The PepsiCo supply chain team should improve quality checks by introducing an automated quality assurance system. This system should be capable of performing real-time analysis and inspection of the incoming raw materials and finished products to detect any inconsistencies or defects (Schermerhorn et al., 2020). Furthermore, an end-to-end traceability system should be implemented to track each product, from the raw material supplier to the final consumer. The company should work with its suppliers to ensure that they meet the required quality standards. Regular audits should be conducted to ensure that the suppliers adhere to the quality standards (Schermerhorn et al., 2020). Finally, the company should invest in employee training and development programs to ensure their employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to carry out quality checks.
The Root Cause of The Problem
Numerous variables contribute to PepsiCo’s supply chain process, which results in the manufacturing of subpar products. Poor management decisions can lead to misallocating resources, resulting in inadequate procurement of raw materials (Schermerhorn et al., 2020). Poor working conditions, such as inadequate safety measures, can lead to lower-quality production. Inadequate technology and outdated machines can lead to inferior products. Unskilled and unmotivated employees can cause production errors, leading to lower-quality outcomes. Unreliable suppliers can lead to supply chain disruptions and poor-quality products (Schermerhorn et al., 2020). Finally, a lack of quality control measures can lead to products of poor quality. PepsiCo’s supply chain method may result in the manufacturing of subpar products as a result of these factors.
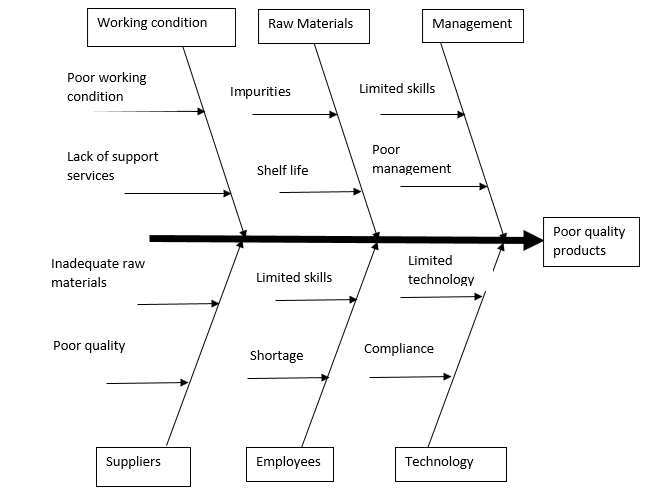
Analysis
Gap Issues in The Supply Chain
PepsiCo’s supply chain can be inefficient due to a variety of factors. The following are the inefficiencies experienced in the process. Firstly, inadequate demand forecasting is among the aspects leading to the issue at the company. PepsiCo’s demand forecasting process is often inaccurate, leading to an inability to plan for production and shipping properly. This can lead to inconsistent product quality and shortages, and overages. Secondly, the organization lacks visibility into its supply chain, making it difficult to identify and address issues quickly. This can result in delayed shipments, poor product quality, and customer dissatisfaction. These factors have contributed to the inefficiencies in the supply chain.
Moreover, other factors lead to inadequacy in the company’s supply chain. PepsiCo’s supplier monitoring system is inadequate, leading to inconsistent product quality due to poor-quality materials or processes. The company’s inefficient distribution network leads to delays and product spoilage. This adversely impacts its supply chain and reduces the quality of products. Poor communication: the company’s inadequate communication system leads to delays and miscommunications between departments. This can lead to quality problems, as well as customer dissatisfaction.
Financial Metrics
The company’s supply chain process leading to the production of products of poor quality has had a major effect on the company’s financial performance. Revenues have declined significantly, with a 7% drop in sales in 2019, compared to the previous year (Shapiro & Hanouna, 2019). The income has fallen, with a 2.3% decrease in the same period. In addition, costs linked with poor-quality supply chain processes have impacted operating expenses, causing an increase of 3.8%. This has decreased the operating margin from 15.7% in 2018 to 13.7% in 2019 (Shapiro & Hanouna, 2019). This all points to a decrease in the company’s profit margin, which has declined from 8.8% to 5.7%. This has severely impacted the organization’s financial health and indicates that it needs to address its supply chain process to improve its products and increase its sales and revenues.
Non-Financial Metrics
PepsiCo produces a wide range of products, from snacks and beverages to cereals and other food items. However, the quality of some of these products has been questioned in recent years, leading to consumer dissatisfaction (Machiels et al., 2019). To measure the current condition of poor-quality products at PepsiCo and to measure success, there are a number of measurable facts that can be used. Firstly, a key indicator of quality is customer satisfaction. PepsiCo can measure customer satisfaction through surveys, feedback forms, and customer service calls (Machiels et al., 2019). By gathering this data, PepsiCo can track customer satisfaction over time and identify improvement areas.
Secondly, a key indicator of the quality of products is customer complaints. Customer complaints can provide feedback on an eminence and help a company identify areas for improvement (Machiels et al., 2019). They can alert a company to potential product problems, such as defective parts or manufacturing issues, that can be addressed and corrected before they become widespread. For example, if a company receives complaints about a particular product feature or design, it can use that feedback to make changes and improve the product (Machiels et al., 2019). PepsiCo can track the number of customer complaints it receives regarding its products and services. This information can be used to track changes in customer satisfaction over time and pinpoint areas that need improvement.
Third, a primary indicator of quality is product returns. By tracking the number of products returned due to quality issues, PepsiCo can measure the success of its quality assurance efforts (Machiels et al., 2019). This information can help the organization identify manufacturing problems, such as faulty ingredients or production processes, to make sure they can be addressed and corrected. In addition, it can indicate customer satisfaction and loyalty, allowing the company to make necessary adjustments to meet consumer needs (Machiels et al., 2019). As a result, tracking the number of returned products can enable PepsiCo to make more informed decisions about product design, packaging, and other aspects of production.
Fourth, PepsiCo can gauge the effectiveness of its quality assurance initiatives by monitoring the quantity of products returned because of quality problems. This metric will provide insight into how the company’s quality control and assurance processes are performing and can be used to identify any potential weaknesses in the system (Machiels et al., 2019). By keeping track of how many products are returned because of quality problems, PepsiCo can take action to find and fix any problems, enhancing product quality and preserving consumer satisfaction (Machiels et al., 2019). Therefore, tracking returns can help PepsiCo better understand consumer preferences and identify areas where the company may need to change its products or processes.
Finally, PepsiCo can track the results of its product testing to ensure that its products meet quality standards. Product testing can help PepsiCo identify potential issues before its products reach consumers, allowing them to take corrective action if necessary (Machiels et al., 2019). This information can be used to gauge the effectiveness of its quality assurance initiatives and pinpoint areas that need improvement. Additionally, PepsiCo can use product testing results to provide valuable insights into consumer preferences, helping them develop more appealing products (Machiels et al., 2019). Therefore, by tracking the effects of product testing, PepsiCo can ensure that its products are consistent with the highest quality and are well-received by consumers.
To Be Condition
PepsiCo’s supply chain can be improved by introducing quality checks when procuring raw materials and forecasting customer needs. As shown in figure 3, quality checks should be conducted on all raw materials to ensure that only high-quality products are used in the production process. Additionally, PepsiCo should use customer data to forecast future needs and adjust production accordingly to prevent over-production and wastage of resources (Srinivas et al., 2021). Furthermore, PepsiCo should invest in training its staff and using technology, such as automated systems, to ensure that the production process is monitored and adjusted in real-time to maintain the highest production standards. Thus, by implementing these measures, PepsiCo can improve the quality of its products and ensure that customers are provided with the highest quality products.
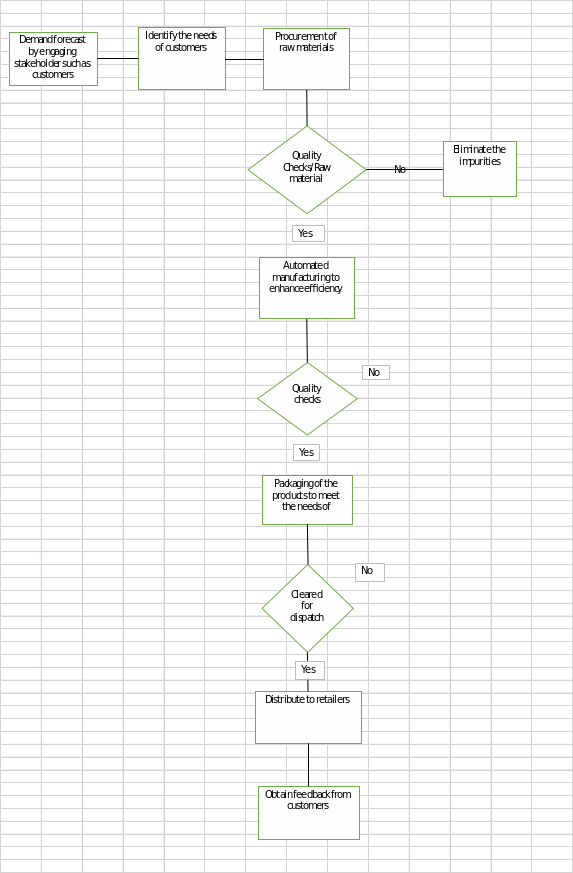
The Benefits of The Proposed Solution
Making changes to improve the quality of products can have a number of benefits for customers, stakeholders, and business operations. Customers will benefit from a better-quality product, reducing the likelihood of issues and complaints (Srinivas et al., 2021). In addition, they will receive a more reliable, efficient, and cost-effective product, and this will save them time, money, and frustration that they may encounter. They will benefit from improved customer service, as a better-quality product will require less maintenance and support (Collier & Evans, 2017). Therefore, stakeholders may benefit from improved customer satisfaction due to better product quality. Increased customer satisfaction can lead to improved customer loyalty, resulting in increased business profits.
From an efficiency standpoint, a better-quality product can lead to fewer returns and fewer problems to address. This means that fewer resources must be devoted to handling customer complaints and product issues (Srinivas et al., 2021). Higher-quality products often require fewer repairs or replacements, reducing the amount of labor and other costs associated with addressing customer issues. Better-quality products can increase customer loyalty and satisfaction, increasing sales and profits (Collier & Evans, 2017). Furthermore, quality products can mean fewer production delays, leading to improved delivery times and a better customer experience. As a result, better quality can lead to fewer repairs or modifications, reducing costs for the business.
From a cost reduction standpoint, better quality products can lead to fewer recalls and warranty replacements, saving a great deal of money. These goods can reduce the need for customer service interactions, which can save money from a manpower and resources standpoint. In addition, quality products may lead to increased customer satisfaction, which can lead to increased sales and customer loyalty, both of which can increase profits (Collier & Evans, 2017). They can last longer and require fewer repairs, saving labour and parts money. Therefore, the products can increase customer satisfaction, contributing to increased sales and higher profits.
The analysis statements presented indicate that there has been improvement in various areas. These include increased customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and profitability (Collier & Evans, 2017). The improved customer satisfaction and operational efficiency have resulted in increased profitability, which is a positive sign for the organization. Furthermore, the decrease in employee turnover and increase in employee engagement suggests that the organization is making strides in creating a positive work environment for its employees (Srinivas et al., 2021). The decrease in customer complaints is a positive sign that the organization is providing better customer service. Therefore, these indicators of improvement demonstrate that the company is making progress.
Recommendations
There are several recommendations for PepsiCo to enhance its supply chain to improve quality products. The company should invest in technologies to facilitate better visibility and tracking of its supply chain activities (Srinivas et al., 2021). This will enable the company to understand the performance of its suppliers and identify potential risks. PepsiCo should develop a comprehensive quality management system to ensure that all its products meet the highest quality standards. This should include proper quality control checks at every stage of the supply chain (Srinivas et al., 2021). PepsiCo should work with its suppliers to ensure they follow the highest standards for materials, production, and other processes. Therefore, this will help the company produce quality products and maintain its reputation as a reliable and trustworthy brand.
PepsiCo should focus on improving its demand forecasting and inventory management to ensure that it is producing the right products in the right quantities. To do this, they should implement automated systems to track sales and customer feedback and analyze consumer trends and preferences (Srinivas et al., 2021). Additionally, they should further invest in data analytics and machine learning to reduce the risk of stock-outs and overstocks. PepsiCo should invest in quality control measures along the supply chain, such as better supplier selection and auditing, to ensure its products are of the highest standard (Srinivas et al., 2021). Therefore, they should invest in training and education for their staff to ensure they have the right knowledge and skills to manage the supply chain effectively.
Conclusion
PepsiCo should make strategic changes in its supply chain to improve the quality of its products. They should focus on increasing collaboration between suppliers, distributors, and customers to ensure that the products are of the highest quality. This can be done by implementing better communication practices, such as regular meetings and better documentation. Additionally, PepsiCo should work with suppliers to develop better quality control measures, such as more rigorous testing of ingredients before they are used in production. Finally, PepsiCo should invest in technologies such as predictive analytics to forecast better demand, which will help them anticipate and prevent potential quality issues. By making these adjustments, PepsiCo can guarantee a more effective and prosperous supply chain while also raising the caliber of its products.
References
Abu-Reidah, I. M. (2020). Carbonated beverages. Trends in Non-Alcoholic Beverages, 1-36. Web.
Bishnoi, R., & Poonam, A. (2020). Embracing Ingenious People Analytics: Case of PepsiCo. International Journal of Management and Humanities (IJMH), 4(6), 150-154. Web.
Collier, D. A., & Evans, J. R. (2017). OM. (6th ed.). Cengage Learning.
Kelloway, C., & Miller, S. (2019). Food and power: Addressing monopolization in America’s food system. Washington, DC: Open Markets Institute.
Li, J., Yang, S., Shi, V., & Zhai, S. (2020). Partial vertical centralization in competing supply chains. International Journal of Production Economics, 224, 107565. Web.
Machiels, C. J., Yarar, N., & Orth, U. R. (2019). Symbolic meaning in beverage packaging and consumer response. Trends in Beverage Packaging, 73-104. Web.
Purkayastha, D., & Rao, A. S. (2017). Case studies in sustainability management. Routledge.
Schermerhorn Jr, J. R., Bachrach, D. G., & Wright, B. (2020). Management (5th ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
Shapiro, A. C., & Hanouna, P. (2019). Multinational financial management. John Wiley & Sons.
Srinivas, S., Rajendran, S., & Ziegler, H. (2021). An Overview of Decisions, Performance and Analytics in Supply Chain Management. Supply Chain Management in Manufacturing and Service Systems, 1-17. Web.
