Ethical values are vital in the nursing field as they facilitate the provision of quality care. In the United Kingdom, the considerations needed to give safe, legal, and moral aid are based on guidelines outlined by the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) under the NMC Code (Nursing and Midwifery Council, 2018). It helps caregivers consider victims’ needs from different angles while maintaining a healthy recovery environment. The guidelines help nurses understand the importance of treating all patients equally while still protecting their privacy rights. Moral consideration is vital among all medics regardless of the practice area. A solid foundation that is needed to make sound choices is established with the presence of these ethical principles.
According to Ellis (2020), ethics are the moral obligations that guide an individual’s behavior, helping them distinguish between wrong and right. Nursing is a profession focused on providing care and encompasses the prevention of sicknesses and promoting health (Grant, Goodman, and Bach, 2019). In the research by Haahr et al. (2019), nursing ethics is defined as the discipline which focuses on addressing sound features of the fostering practice. Nurses are trained to care for the injured or sick (Ilkafah, Mei Tyas, and Haryanto, 2021). Ethical considerations in nursing are principles and values that guide health practitioners in decision-making concerning better care provision (Haahr et al., 2019).
This paper’s primary focus will be on the justification and understanding of how literature is searched with close reference to the ethical nursing considerations topic. The outline of the subjects to e covered thoroughly throughout the paper includes contextual information on moral practitioner deliberations, a description of how the literature search is conducted, and a research critique framework. Other segments to be discussed are the importance of literature searching and appraisal in nursing and a summary of the main points under the conclusion.
Ethical Nursing Practices
Nurses must find balance while providing patient care, which can be promoted by adhering to ethics. The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) was formulated in 2001 by the Health Act 1999 to regulate nurses, midwives, and nursing associates (Connell et al., 2022). The NMC Code sets the guidelines for ethical nursing care. Its primary function is directing all practitioners on the professional motives to uphold while providing treatment. Four core principles guide the ethical considerations in the NMC Code: prioritise people, practise effectively, preserve safety, and promote professionalism and trust (Nursing and Midwifery Council, 2018). Many healthcare facilities, medical centres, and hospitals have ethics committees to resolve moral conflicts and dilemmas (Stievano and Tschudin, 2019). The International Council of Nursing (ICN) performs similar functions to the NMC globally. It has a steering committee that revises the ethical guidelines set (Stievano and Tschudin, 2019). Medical practitioners are responsible for identifying and recognising moral setbacks affecting patients and the staff.
The ‘ethical nursing practices’ topic is critical to caregiving as it outlines the strategies for providing quality care. They include caregiving, moral resilience, distress and courage, advocacy, and end-of-life issues (Varkey, 2021). Morale is improved, and risks that arise from unethical practices are reduced when a culture of morality customs gets established (Aveyard and Sharp, 2017; Haahr et al., 2019). This literature search aims to explore various scholarly articles from different databases focusing on ethical nursing guidelines, thus helping get the best available information.
Search strategy
The literature search was conducted by providing a straightforward review question that formed the basis of the analysis. Various databases and search engines were used on the internet where specific articles were identified after keying in some terms. The question that guided the literature review was: what is the importance of the moral guidelines stated under the NMC Code in the United Kingdom? The search terms used to help identify the relevant sources include professional ethics, dilemmas in medicine, nursing, ethical consideration, healthcare morality, and the code of ethics for nurses. GoogleScholar was the primary search engine used to identify the scholarly articles related to the topic, and the databases used included PubMed, JSTOR, and ScienceDirect.
Applying inclusion and exclusion criteria made it easy to identify the most valuable research studies and those with minimal information related to the topic, making them invaluable. The two standards were determined after stating the literature review question and before more research was started. Scoping searches were conducted to further determine appropriate sources by gaining an overview of the depth of the analysis undertaken in the studies. The encompassing basis stated all the information a research work needed before getting included. Factors that would make a source ineligible were identified under the exclusion scale. The standard criteria used in both were: language, relevance, redundancy, publication, and scholarly review. The language used in the studies should be English; those in foreign were excluded. Research works with any form of duplicity were excluded from the consideration. Accepted research articles were those published within five years. Peer-reviewed sources were highly considered as they consisted of information vetted and analysed by other professionals in the field.
The number of papers identified to be reviewed was 30, which went through the stages like screening and eligibility tests. Some were excluded at each stage if they failed to meet the expected criteria.
PRISMA Flowchart
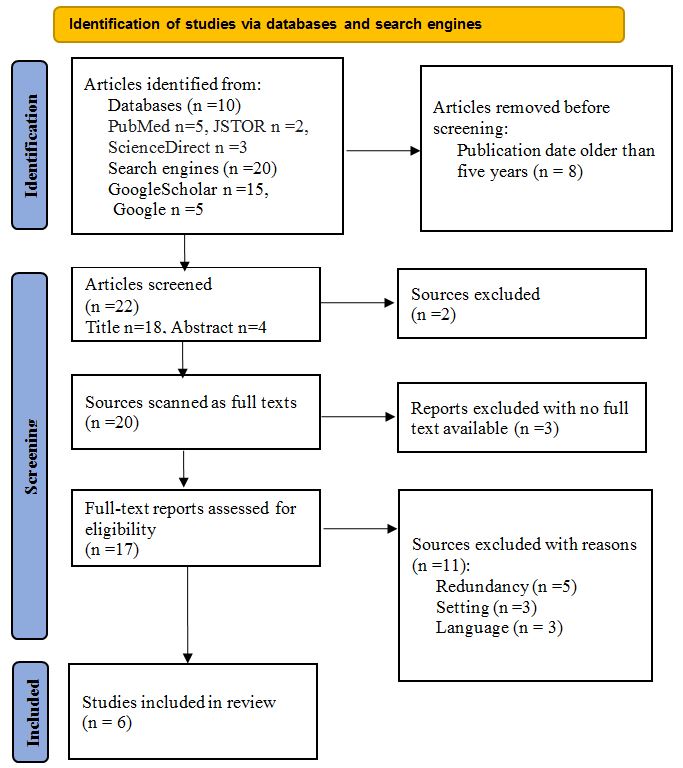
Eight research works were removed before the screening process as they were considered old studies. Required journals must be current and issued within the last five years. The remaining were screened using the title and abstract, eliminating two sources as they failed to display information vital to the topic. Twenty remaining articles were retrieved and thoroughly scanned as full texts. Three reports were excluded as no full texts of the stated sources existed for free. There was a need to pay to get full access to the articles, which was a challenge. Given the nature of the study, the abstract information was not sufficient.
Complete scanning was conducted on the remaining articles before including the potential sources in the systematic review. The following reasons resulted in eliminating some reports: redundancy, setting, and language. As a result, five papers that had duplicate data with minor changes in some sections were excluded. Three journals had participants outside the desired location, a healthcare facility, thus making them ineligible. The language barrier was witnessed as some articles were written in foreign languages, and only the abstract and title were in English. Preferred reports were written in American or British English for easy understanding and analysis. After excluding those that lacked relevance, the six desired works were identified and were to be used in the review.
The Research Critique Framework
Potential Implications
A literature search is vital in identifying potential sources for a specified topic, and the appraisal helps distinguish between valuable reports and those with low-quality information. It provides insight into how previous scholars studied a subject (Bramer et al., 2018). It helps recognise opportunities, detect shortcomings, and interpret data (Bramer et al., 2018). Through it, it was possible to identify sources and past researches that focused on identifying ethical nursing considerations. The impacts of evaluating the literature sources include reducing the burden of study by allowing one to focus on more relevant articles with high-quality information related to ethics in nursing. Through this, the number of vital works directly related to the principles of ethics in nursing was reduced to six from the potential thirty papers.
Nursing is a broad topic and contains varying information that can be included in current research from past works. Adopting a literature inquiry is crucial as it will help identify all articles, reports, and other relevant sources (Bramer et al., 2018). It enables one to scan and only select works directly linked to nursing and not any other discipline. It provides insight into how previous researchers studied the field, which is vital in recognising opportunities. Critical appraisal here is relevant in eliminating weak nursing studies. It further helps distinguish evidence from opinions, beliefs, and assumptions, especially since the field of study is critical to human well-being.
Conclusion
The literature search was vital in selecting relevant information for analysing the topic, ‘Ethical Nursing Considerations.’ Specific search terms like nursing, ethical consideration, and professional ethics were used to locate the research works. The search engine and databases used included GoogleScholar, PubMed, JSTOR, and ScienceDirect. The inclusion and exclusion criteria focused on the publication, scholarly review, and relevance were used to seek out the selected sources. The PRISMA Flowchart summarises the steps followed in determining the sources. A critical appraisal was done, under which three papers were evaluated based on several assessments to assert their relevance. The literature searches and evaluation are effective in the nursing field and the selected topic as it helps select works with relevant information and exclude others.
Reference list
Aveyard, H. and Sharp, P. (2017) A beginner’s guide to evidence-based practice in health and social care. 3rd edn. London: Open University Press.
Bramer, W. M. et al. (2018) ‘A systematic approach to searching: an efficient and complete method to develop literature searches’, Journal of the Medical Library Association, 106(4), pp. 531–540. Web.
Connell, C. et al. (2022) ‘Mental health nursing identity: a critical analysis of the UK’s Nursing and Midwifery Council’s pre-registration syllabus change and subsequent move towards genericism’, Mental Health Review Journal, 27(4), pp. 472–483. Web.
Ellis, P. (2020) Understanding ethics for nursing students. 3rd edn. London: Sage.
Grant, A., Goodman, B. and Bach, S. (2019) Communication and interpersonal skills in nursing. 4th edn. Los Angeles: Learning Matters.
Haahr, A. et al. (2019) ‘Nurses experiences of ethical dilemmas: a review’, Nursing Ethics, 27(1), pp. 258–272. Web.
Ilkafah, I., Mei Tyas, A. P. and Haryanto, J. (2021) ‘Factors related to implementation of nursing care ethical principles in Indonesia’, Journal of Public Health Research, 10(2). Web.
Nursing and Midwifery Council (2018) ‘The Code: Professional standards of practice and behaviour for nurses, midwives and nursing associates’. London: Nursing and Midwifery Council. Web.
Stievano, A. and Tschudin, V. (2019) ‘The ICN code of ethics for nurses: a time for revision’, International Nursing Review, 66(2), pp. 154–156. Web.
Varkey, B. (2021) ‘Principles of clinical ethics and their application to practice’, Medical Principles and Practice, 30(1), pp. 17–28. Web.
