Introduction
Among the very many diseases that affect the central nervous system of human beings is Parkinson’s disease. Persons suffering from this degenerative disorder have their motor skills, speech, and other central nervous system functions greatly impaired. Medics classify Parkinson’s disease under the class of movement disorders.
This is because the disease causes numerous movement abnormalities as characterized by its symptoms. For example, persons suffering from this disease experience muscle rigidity, palpitation, gait and postural aberrations. The disease can also reduce the speed of physical locomotion among affected human beings, a condition doctors call bradykinesia.
Furthermore, if not discovered earlier enough, the patient can loose physical movement, akinesia, subjecting the person to a wheelchair. It is quite imperative to understand that the central nervous system that encompasses the brain and the spinal cord runs the whole lot that a human being does, including moving.
However, the disease causes movement disorders in human beings, as the affected central nervous system gradually fails to control body movements. In neurology, the brain has nerve cells responsible for body movements-basal ganglia. Parkinson’s disease destroys these nerve cells reducing a person to an armature. Consequently, the brain fails to produce dopamine, which will instruct other parts of the brain to synchronize body movements.
This means that persons suffering from this degenerative disorder have extremely low levels of dopamine hence; the body does not receive the full information required for movement to occur. The paper examines how Parkinson’s disease affects the body, its symptoms, treatment and diagnosis, the preference group, and the expected results if patients get a massage (Jankovic, 2007, 368-376).
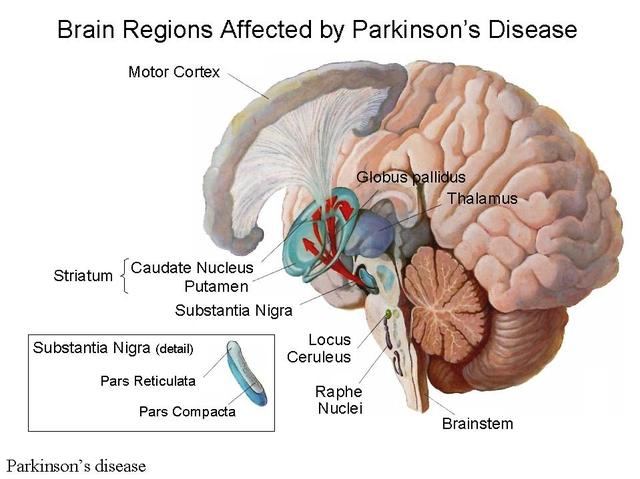
Signs and Symptoms
Persons suffering from Parkinson’s disease (Parkinsonism) exhibit many signs and symptoms but not reduced to physical movement. For instance, medics classify this disorder into four subtypes namely: idiopathic Parkinsonism acquired Parkinsonism, genetic Parkinsonism, and multiple system degeneration Parkinsonism. Whatever the origin, Parkinson’s disease causes harm to the person’s ability to move and eventually causes motor symptoms.
Although medical practitioners agree that it is the damage of the dopamine cells that leads to symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, there is a controversy on how the nerve cells responsible for its production get damaged. This is the reason why some medics are involved in researching possible genes that could shed some light on the real cause of Parkinson’s disease. Some theoretical explanations also point to environmental factors such as pesticides and chemicals as the cause of nerve damage.
This disorder is not contagious. However, some research indicates that it is hereditary and that both men and women can get the disease. Nevertheless, statistics indicate that the number of men suffering from Parkinson’s disease is higher than that of women.
Persons suffering from Parkinsonism exhibit tremors and trembling to mean that they cannot hold something in their hands. Additionally, these persons find it difficult to walk from one place to another, as it is intricate for them to maintain balance and coordination. Other symptoms include standing problems, stiff joints and sluggishness.
As time goes by, other symptoms become prevalent. For instance, since the disease destroys brain nerve cells that produce dopamine, patients can lose the ability to perform other functions like swallowing, talking, or even smiling. With the absence of dopamine, such patients become expressionless although they have feelings. Sometimes, persons suffering from this disease find it difficult to remember past happenings or even think.
Since the disease mainly affects the balance and physical movement of persons, persons suffering from this disease fall down easily and can break bones. It is vital to note that the disease normally affects people aged 50 and above. The symptoms develop gradually meaning, persons suffering from this disease can have a prolonged life. In some circumstances, patients can experience secondary symptoms such as constipation, sleep disturbances, dementia and breathing quandaries (Slavin, 2010, p.1).
Medications
So far, no single research indicates the cause of Parkinson’s disease. In addition to this problem, there is no cure for this disease. Nevertheless, medics assert that intensive exercise can prevent further symptom development and instead, maintain balance and mobility. Physical exercises like walking, jogging, and dancing can stimulate the production of dopamine aimed at maintaining balance and mobility. Additionally, Parkinson’s disease patients risk getting osteoporosis as they lack vitamin D. nevertheless, medical practitioners advocate exercises such as lifting weights aimed at reducing the chances of developing osteoporosis.
In Europe and America, institutions such as Food and Drug Administration (FDA) propose the implantation of surgical devices aimed at reducing tremors. Research shows that the process of medication for this disease is experimental and takes a lot of time. This is because the disease has progressive symptoms, which requires different medications according to the current modification.
Drug Therapies
Medics prescribe drugs aimed at maintaining the dopamine levels. However, the drugs change with the complexity of the symptoms. The two main drugs that doctors use to treat the disease are Levodopa and Carbidopa. When injected into the body, Levodopa turns into dopamine and takes the place of the absent natural dopamine.
On the other hand, Carbidopa helps the body in slowing down the conversion of Levodopa outside the brain region, hence, maintaining the level of dopamine in the brain. In most cases, the drugs are not effective because with time, the body fails to convert Levodopa into dopamine; a situation that causes reflex movements, dyskinesia.
Massage Therapy
Medical research indicates that massage is beneficial to persons suffering from Parkinson’s disease. Since Parkinson’s disease, mainly causes muscle inflexibility and rigidity, it is important to perform bodywork activities in order to reduce muscle and joint stiffness. These activities will induce sensation in the areas of interest and help to correct the present incongruities.
Nevertheless, as Nicole (2007) notes, there has emanated serious controversies on this type of therapy, as some medics do not prefer it. For instance, these medics believe that this is a complex therapy cumbersome for many patients. Furthermore, this disease is a central nervous dysfunction, which cannot be resolved through physical activities. On the other hand, massage can cause side effects such as antidepressants making it sometimes unsuitable.
However, massage plays a key role in controlling involuntary movements hence, ensuring patient safety. Additionally, massage plays a vital role in relieving therapeutic symptoms. For example, since many patients suffering from this Parkinson’s disease experience harsh muscle twinge and rigidity, massage therapies can alleviate these problems. Research done by various medics indicate that regular massage therapies help in plummeting tremors and improves the ability of the body to function normally (p.1).
Medical experts from the University of Miami’s Touch Research Institute did an experimental research to determine how massage helps in relieving symptoms of patients suffering from Parkinson’s disease. They found out that massage helps these patients to resume their daily functioning, while suppressing the stress-hormone levels. This research group subjected 16 adults suffering from this disease into massage therapy.
These 16 patients received a 30-minute massage therapy twice a week for a period of five weeks. Medics divided the 30 minutes into two equal sessions, where patients received massage while under prone position and the other session on supine position. Since communication was paramount, the doctors used music from a cassette tape to guide the relaxation of muscles. This activity went on for five weeks. After the fifth week, the doctors examined patients on daily functioning, the time patients slept, and the general physical fitness of the body. They also collected urine samples aimed at determining the stress-hormone levels of these patients.
The report indicated that the daily functioning of these patients improved greatly. Moreover, test results from urine samples showed a decline in stress hormone levels, that is, the level of norepinephrine and epinephrine decreased significantly. On the other hand, the results showed an increase in dopamine production hence, making massage one of the preferred methods of easing pain in patients suffering from Parkinson’s disease (Hernandez-Reif, Tiffany, Shay & Christy, 2002, pp. 187-182).
Conclusion
Although massage helps patients to relax and perform their daily functioning, it is better to perform it from qualified practitioners. This is because patients suffering from this disease and under medication should not undergo massage as it can render side effects.
With the development of medicines such as Levodopa and Carbidopa, patients can increase their dopamine levels and perform their daily functioning, have relaxed muscles, and maintain balance and mobility. Overall, occupational therapy practices such as massage are very instrumental in easing the muscle pain and joint rigidity experienced by Parkinson’s disease patients.
Reference List
Hernandez-Reif, M., Tiffany, F., Shay L. & Christy, C. (2002).Massage Reduces Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies, 6(2), 177-182. Web.
Jankovic, J. (2008). Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 79(4), 368–376. Web.
Nicole, C. (2007). The Benefits of Massage Therapy on Parkinson’s disease. Web.
Slavin, J. (2010). Massage and Parkinson’s disease: A Few Lessons Learned. Massage Today, 6(10). Web.
